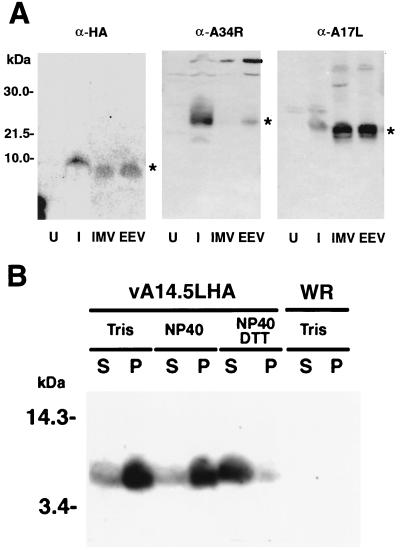
FIG. 5.
Association of the A14L-HA protein with the membrane fraction of virus particles. (A) BS-C-1 cells were mock infected or infected with 10 PFU of vA14.5LHA per cell. After 18 h, the medium was harvested, and the cells were disrupted with a Dounce homogenizer. Virus particles were purified by sedimentation through a sucrose cushion and CsCl centrifugation (23). The virus band was diluted with Tris-HCl (pH 9), collected by centrifugation, and resuspended in Tris buffer. The lysates of mock-infected cells (U) or infected cells (I) were analyzed in parallel with CsCl gradient fractions by SDS-PAGE and Western blotting with MAb 12CA5 (α-HA) or polyclonal antibody to the A34R protein (α-A34R) or A17L protein (α-A17R). Fractions containing IMV and IEV or EEV are indicated. Small differences in the electrophoretic mobilities of proteins from lysates and CsCl gradients could be due to the ionic strengths. The bands corresponding to A14.5L-HA, A34R, and A17L are indicated by asterisks. The positions and masses of marker proteins are indicated to the left. (B) Vaccinia virions, purified by sucrose gradient centrifugation (9) from cells infected with vaccinia virus WR or vA14.5LHA, were incubated with 10 mM Tris (pH 7.4) or 1% NP-40 in 10 mM Tris (pH 7.4) in the presence or absence of 10 mM dithiothreitol. Soluble (S) and insoluble (P) fractions were separated by centrifugation and resuspended to equal volumes in SDS-containing sample buffer. An equivalent amount of each fraction was subjected to electrophoresis, and the separated proteins were transferred to a membrane and analyzed by Western blotting with anti-HA MAb 12CA5.