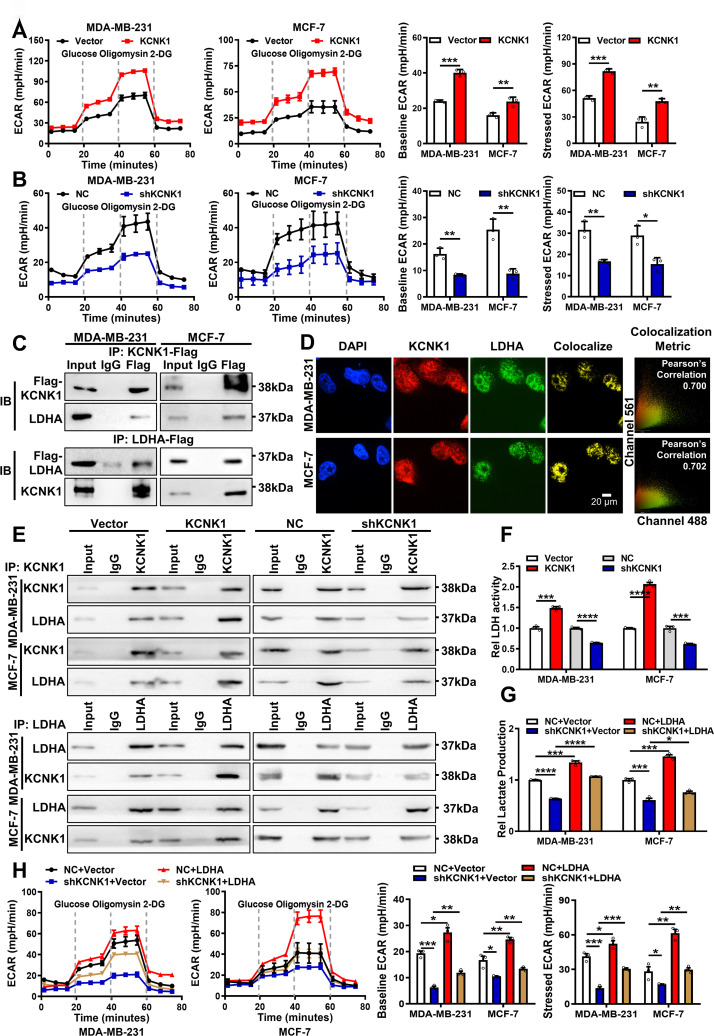
Fig 3. KCNK1 promotes metabolic reprogramming in breast cancer cells via binding to and activating LDHA.
(A) The ECAR was measured by the Seahorse XF assays in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells after KCNK1 overexpression (left); baseline ECAR and stressed ECAR were calculated based to the total ECAR (right). (B) The ECAR was measured by the Seahorse XF assays in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells after KCNK1 knockdown (left); baseline ECAR and stressed ECAR were calculated based to the total ECAR (right). (C) The interaction between KCNK1 and LDHA was examined by immunoprecipitation using an anti-Flag antibody in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells transfected with Flag-KCNK1 or Flag-LDHA vector, followed by western blotting using the anti-KCNK1 or anti-LDHA antibodies. (D) Immunofluorescence experiments showed that KCNK1 and LDHA were co-localized in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells. DAPI-stained nucleus: blue; anti- KCNK1: red; anti-LDHA: green; the colocalize image represents the overlap of KCNK1 and LDHA (scale bar: 20 μm). (E) Quantitative Co-IP experiments showed that KCNK1 overexpression enhanced their binding capacity while KCNK1 knockdown reduced the capacity. (F) The lactate dehydrogenase activity was detected in breast cancer cells after overexpression or knockdown of KCNK1. (G) The lactate production ability of breast cancer cells was detected after KCNK1 knockdown, LDHA overexpression, and co-transfection of shKCNK1 and LDHA overexpression vectors. (H) The ECAR was measured by the Seahorse XF assay in MDA-MB-231 and MCF-7 cells after KCNK1 knockdown, LDHA overexpression, or co-transfection of shKCNK1 and LDHA overexpression vectors (left); baseline ECAR and stress ECAR were calculated from total ECAR (right). All experiments were triplicated. Data are presented as mean ± SD, analyzed by unpaired two-sided t tests. Source data are provided as S1 Data. ECAR, extracellular acidification rate; LDHA, lactate dehydrogenase A.