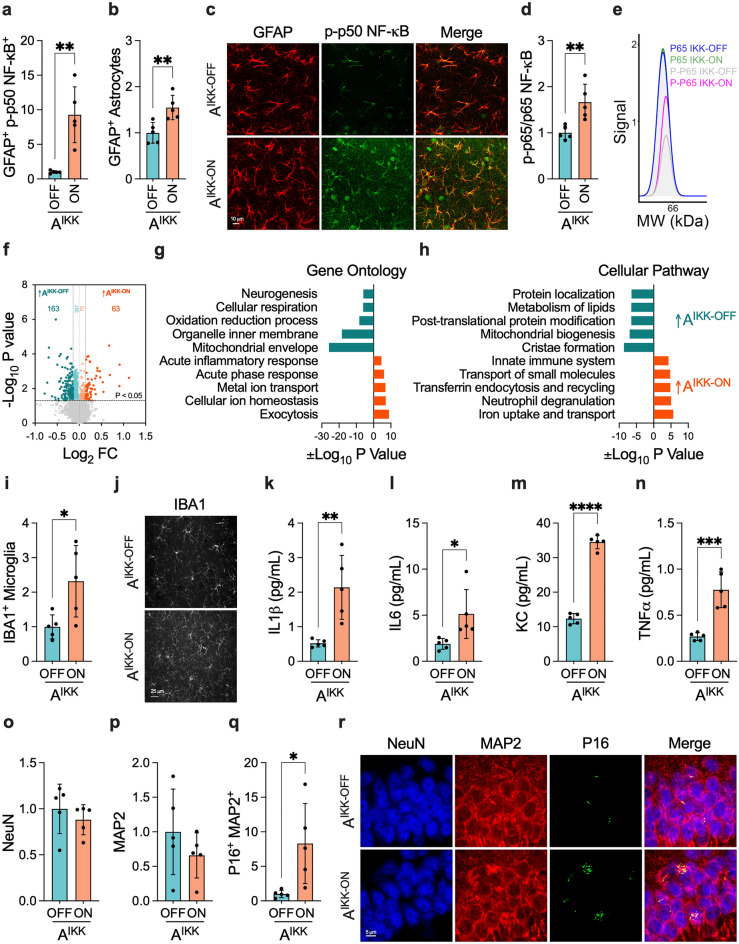
Figure 2.
Changes in the healthy hippocampus caused by sustained astrocytic IKK2 activation. (a, b) Volumetric analysis of (a) p-p50 NF-κB in GFAP+-astrocytes (n = 5 per group, six 3D images per mouse) and (b) overall GFAP+-astrocytes (n = 5 per group, nine 3D images per mouse). (c) Illustrative images of p-p50 NF-κB and GFAP staining patterns. (d) Overall levels of p-p65 NF-κB normalized by total p65 NF-κB in hippocampal lysates (n = 5 per group). (e) Representative images of chemiluminescence signal detected at 65 kDa. (f) Volcano plot of targeted pairwise expression analysis between AIKK-OFF and AIKK-ON mice (n = 4–5 per group). (g, h) Differentially expressed proteins were analyzed using the GSEA software to determine the enrichment of (g) gene ontology and (h) cellular pathways terms. (i, j) Comparison of IBA1+-microglia between AIKK-OFF and AIKK-ON mice (n = 5 per group, three 3D images per mouse). (k–n) Levels of (k) IL1β, (l) IL6, (m) KC, and (n) TNFα in T-PER soluble hippocampal lysates (n = 5 per group). The levels of IFNγ, IL2, IL4, IL5, IL10, and IL12p70 were below the sensitivity of the multiplex kit. (o–r) Volumetric analysis of (o) NeuN (n = 5 per group, six 3D images per mouse), (p) MAP2 (n = 5 per group, six 3D images per mouse), and (q) P16+ MAP2+ (n = 5 per group, three 3D images per mouse) and (r) representative images in AIKK-OFF and AIKK-ON mice. Data were analyzed through an unpaired t-test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001.