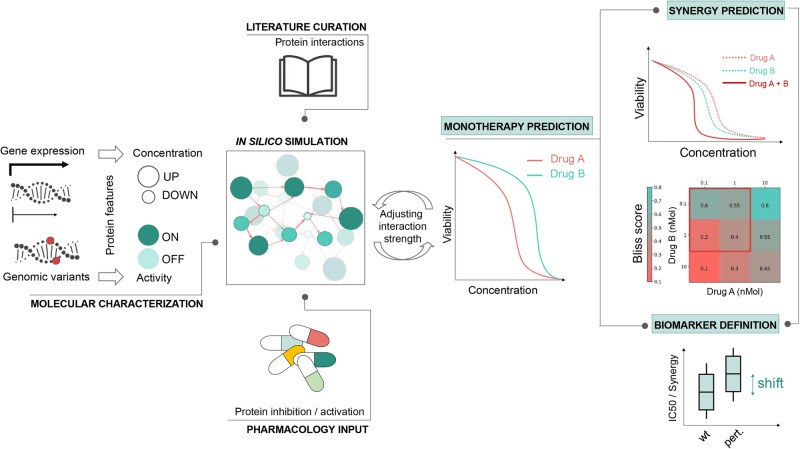
Fig. 1. Integration of diverse data types to feed our Simulated Cell to elucidate drug-specific biomarkers as well as to help understand the mechanism of predicted synergy.
By using cell line-specific genomic and transcriptomic data, the Simulated Cell can be transformed from a general wiring diagram to a network-based in silico replica of a cancer cell line. It carries its characteristic mutations beside cell line-specific expression patterns which modify the effect of a node by the binary activity and continuous concentration parameter changes, respectively. Available molecular compound target profiles enable pharmacological perturbation of the signaling network in a dose-dependent and compound-specific manner by modifying the concentration parameter of primary and off-targets of drugs included in the protein-protein interaction network. This approach generates insights into the activity of affected pathways after drug exposure and predicts the cell line’s response to a given intervention by calculating IC50 values and dose-dependent changes in viability. Each Simulated Cell is calibrated to match its in vitro counterpart’s IC50 value accurately. This is achieved by setting up the adequate and proportionate contribution of each regulator of a given protein so biological hypotheses are recapitulated on the level of protein interactions that leads to the accurate pathway level signal propagation, and ultimately correct survival response. After the calibration process to establish the network parameters and enable in silico experiments, cell line-specific responses of the Simulated Cell to a certain combination therapy–measured by combination synergy and combination-specific viability–are strictly trained on the monotherapeutic effect of the combination partners. By inducing artificial protein alterations, affecting protein activity and/or concentration, combination-specific biomarkers and their effect on combination synergy and cell viability can be identified.