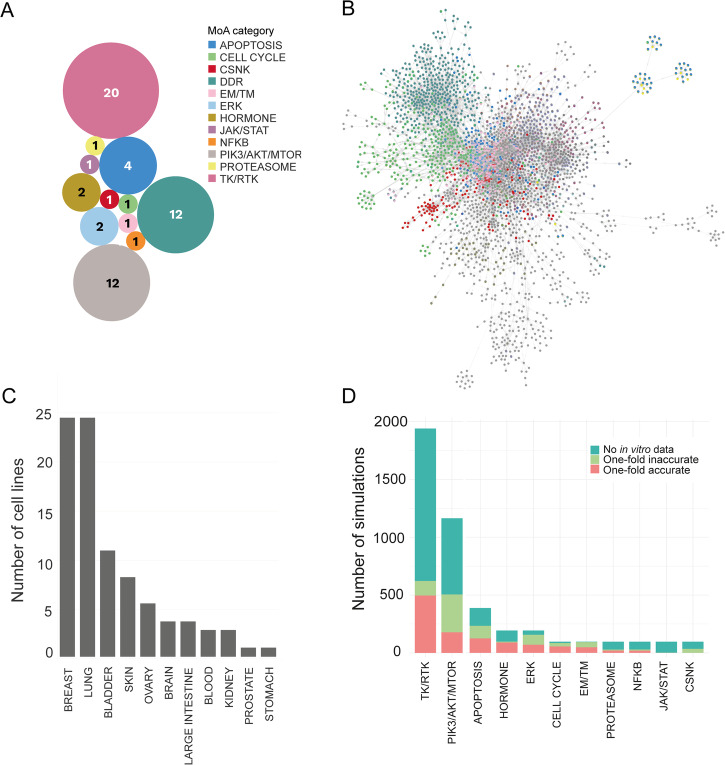
Fig. 2. The simulated cell encyclopedia and proportions of accurate and inaccurate simulations across the predicted monotherapy landscape.
A Compound library of the presented combinations. The compounds were categorized into MoA groups based on the pathway membership of primary drug targets with the lowest binding affinity. B Snapshot of the network functioning in the Simulated Cell. Our Simulated Cell is based on a graph, where proteins and cellular events are represented as nodes and the physicochemical properties of their interactions are represented as edges between them. DDR pathway members are highlighted in coral, while survival-related pathways, such as different parts of the cell cycle, are colored turquoise. In the model version used for this analysis, our network included 56 modules covering the main cancer-driving pathways with a total of 1997 nodes and 5004 interactions, out of which 14 modules cover the DDR-related mechanisms. C Indications covered by cell lines during in silico experiments. The cell lines were grouped into indications according to the localization of the primary tumor which the cell line was derived from. D Proportion of accurate and inaccurate in silico monotherapy predictions compared to in vitro measurements (from public sources, not from the DREAM dataset) in mechanism of action (MoA) categories. The Y-axis shows the overall number of simulations, regardless of the in vitro value availability and mechanism of action groups are ranked by the number of one-fold accurate predictions. Unfortunately, due to the low in vitro data coverage, there are many cases where benchmarking was not possible. Accurate range was defined as |log10(IC50in vitro) - log10(IC50in silico)| <1), meaning the measured in vitro IC50 is in the range of (IC50in silico / 10, IC50in silico * 10) covering an interval of two orders of magnitude. This level of accuracy reflects the variability between two in vitro data points in repeated experiments. On the MoA level, the most accurate groups were the TK/RTK and PIK3-AKT-MTOR. CSNK Casein kinase, DDR DNA damage repair, EM/TM Epigenetic/Transcriptomic modulation, ERK extracellular signal-regulated kinase, JAK/STAT Janus kinase/signal transducers and activators of transcription, NFKB NF-kappa B, PIK3/AKT/MTOR Phosphatidylinositol 3’ -kinase(PI3K)-AKT-mTOR, TK/RTK tyrosine kinase/receptor tyrosine kinase.