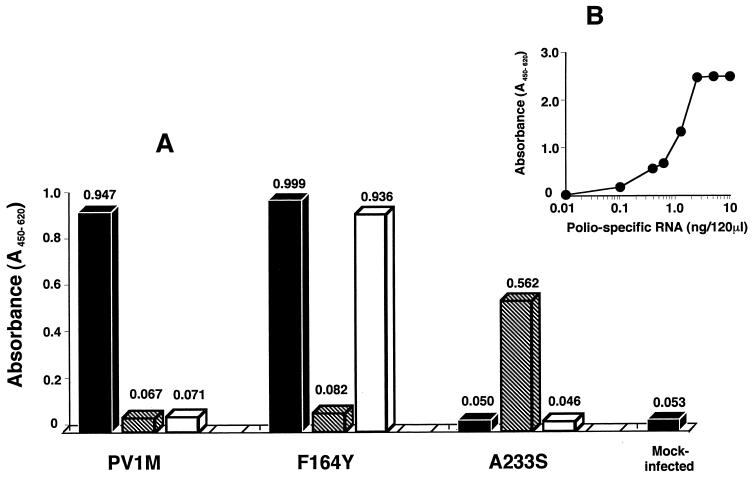
FIG. 4.
Effect of MRL-1237 and guanidine on poliovirus-specific RNA synthesis. Poliovirus-specific RNA synthesis in virus-infected HeLa cells was determined by the Northern ELISA assay described in Materials and Methods. (A) The HeLa cell monolayers were inoculated with a wild-type PV1(M) virus, with an MRL-1237-resistant PV1(M)2C-F164Y virus, or with a guanidine-dependent PV1(M)2C-M187L/A233S virus. The infected cells were incubated in MEM without drug (solid bar), with 2 mM guanidine (striped bar), or with 50 μM MRL-1237 (open bar) for 5 h. The extracted RNAs were biotinylated, and 100 ng of biotinylated RNA per 130 μl was hybridized with 100 ng of a DIG-labeled poliovirus-specific DNA probe. Finally, the biotinylated poliovirus-specific RNA was visualized by the peroxidase-tetramethylbenzidine system. The viral RNA production is presented as the mean OD450–620 (the absorbance at 450 nm with a reference wavelength of 620 nm) values of three individual RNA samples. Total RNA from mock-infected cells was also prepared as a negative control. (B) Poliovirus RNA was transcribed from a pVMT7(1)pDS306(T) clone and biotinylated as a positive control. The OD450–620 values were determined with dilutions of the biotinylated poliovirus RNA.