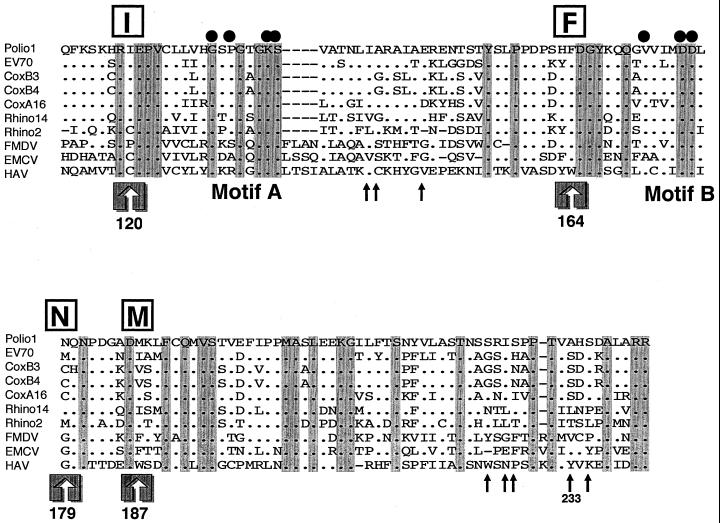
FIG. 5.
Amino acid alignment of the NTP-binding motif of the 2C proteins of picornaviruses. The sequence data were obtained from the GenBank sequence database. The names of virus species are abbreviated as follows and the GenBank accession number is shown in parentheses: polio1, Mahoney strain of poliovirus type 1 (J02281); EV70, J670/71 strain of enterovirus 70 (D00820); coxB3, Nancy strain of coxsackievirus B3 (M16560); coxB4, JVB strain of coxsackievirus B4 (X05690); coxA16, G-10 strain of coxsackievirus A16 (V05876); Rhino14, 1059 strain of human rhinovirus type 14 (K02121); Rhino2, HGP strain of human rhinovirus type 14 (X00429); FMDV, Argentine/61 strain of foot-and-mouth disease virus A10 (K02990); EMCV, R strain of encephalomyocarditis virus (M81861); HAV, LA strain of human hepatitis A virus (K02990). Amino acids are numbered from the amino terminus of the 2C protein of poliovirus type 1. The consensus A and B motifs of the NTP-binding proteins are indicated. Solid circles indicate amino acids critical for the viral replication of poliovirus, as previously demonstrated by site-directed mutagenesis (47, 70). Highly conserved amino acid residues among 10 picornavirus strains are shaded in gray. Major phenotypic determinants for drug resistance or dependence (Ile-120, Phe-164, Asn-179, and Met-187) are indicated as I, F, N, and M (boxed) and by large arrows. The minor determinants responsible for guanidine phenotypes are indicated by small arrows (72).