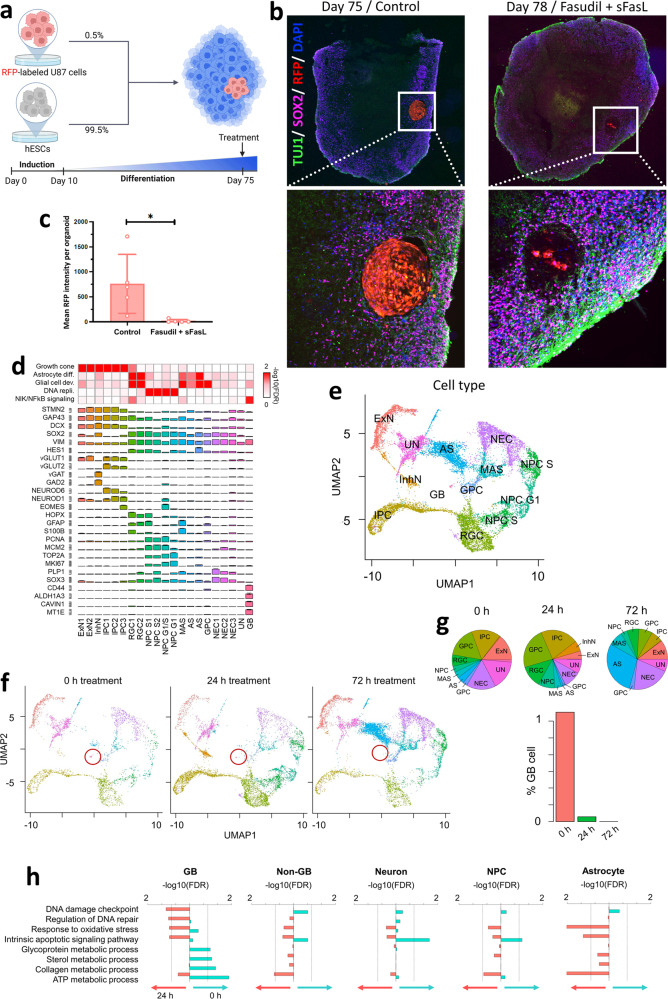
Fig. 4. Fas-mediated apoptosis targets glioblastoma in a brain organoid model.
a Cortical brain organoids were formed by culturing human embryonic stem cells (hESCs, 99.5%) with red fluorescent protein (RFP)-expressing U87 glioblastoma cells (0.5%). b–c Seventy-five-day-old organoids were imaged using spinning disk fluorescence microscopy, where the glioblastoma mass could be distinguished using RFP signal. Upon treatment with fasudil+sFasL, the RFP-expressing regions had almost disappeared by day 78 (p = 0.022; unpaired t test). d–e Cell types in the uniform manifold approximation and projection (UMAP) plot of glioblastoma brain organoids. ExN: excitatory neurons, InhN: inhibitory neurons, IPC: intermediate progenitor cells, RGC: radial glia cells, NPC: neural progenitor cells, MAS: mature astrocytes, AS: astrocytes, GPC: glial progenitor cells, NEC: neuroepithelial cells, UN: unknown cell type, and GB: glioblastoma cells. f UMAP plots of glioblastoma brain organoids after 0, 24, and 72 h of treatment with fasudil+sFasL. The glioblastoma cluster (circled in red) shrank and eventually disappeared. g Percentages of varying cell types in the organoid at the three different time points. The percentage of GB cells approached zero after 72 h of treatment. h After 24 h of fasudil+sFasL treatment, the expression of genes related to apoptotic pathways, DNA damage, and oxidative stress increased in GB cells, but that of genes related to metabolic processes decreased.