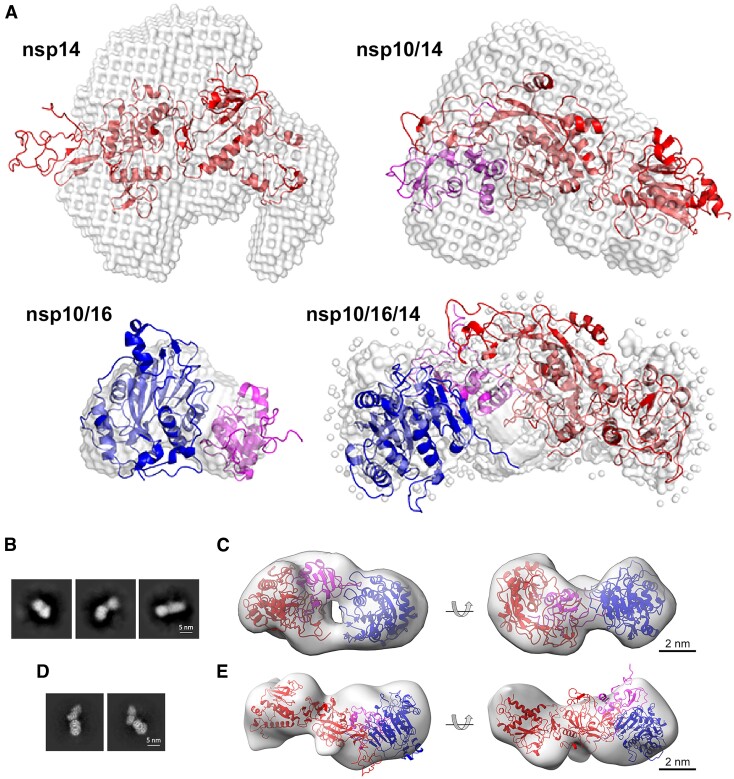
Figure 6.
Heterotrimer structural characterization. (A) Molecular envelopes representing the experimental SAXS scattering profiles of nsp14wt (PDB ID: 7R2V), nsp10/14wt (PDB ID: 5C8U), nsp10/16 (PDB ID: 6W4H), nsp10/16/14wt (model generated using SREFLEX software). Overlaid are the best fits of crystallographic/theoretical models of relevant complexes. Color coding: nsp10 in magenta, nsp14 in red, nsp16 in blue, molecular envelopes in gray. (B) Transmission electron microscopy (TEM) characterization of the nsp10/16/14ExoN complex. Representative 2D classes obtained by template-free 2D classification of particles picked from NS-TEM micrographs. (C) Rigid body fit of SAXS-derived structure of heterotrimer complex into NS-TEM-derived 3D reconstitution map. Nsp14ExoN, nsp10, and nsp16 are represented as red, magenta, and blue ribbon models, respectively. The 3D reconstitution map is shown as transparent gray surface. (D) 2D classes obtained from particles from cryo-EM and the corresponding 3D volume (E). The size and shape of ab initio reconstituted density agrees with the expected heterotrimer structure. Significant dynamics of the complex prevented higher resolution analysis.