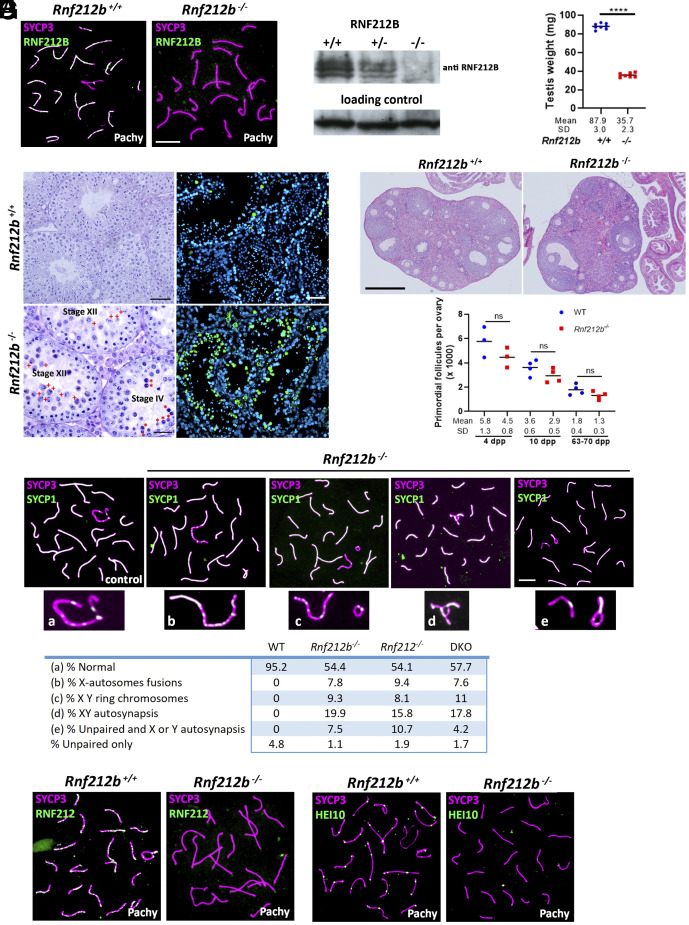
Fig. 4.
Characterization of Rnf212b-deficient mice. (A) Double immunolabeling of RNF212B and SYCP3 showing absence of fluorescent signal in the Rnf212b−/−and foci labeling in the control spermatocytes. Bar 10 μm. (B) Western blot analysis of whole testis extracts showing two bands in the wild type and heterozygous that are absent in the Rnf212b−/−. (C) Plot representation of the reduction in the weight of the testis from Rnf212b−/−in comparison with the wild-type (WT). (D) Left panel, histological section of a testis from Rf212b+/+ and Rf212b−/−mice showing abnormal accumulation of tubules at stage XII of the seminiferous epithelial cycle with abnormal and apoptotic metaphase I cells (red crosses) and at stage IV of the seminiferous epithelial cycle having apoptotic pachynemas (red asterisks). Bar 50 μm in Rnf212b+/+and 25 μm in Rf212b−/−. Right panel, immunofluorescence detection of apoptotic cells by TUNEL staining showing an increase of apoptotic cells in Rf212b−/−seminiferous tubules. Bar 50 μm. (E) Upper panel, histological staining of representative sections of ovaries from an Rnf212b+/+and an Rnf212b−/−adult mice, showing oocytes and follicles at all stages of follicular development. Bar 200 μm. Lower panel, representative plot of primordial follicles quantitation from Rnf212b−/−and wild-type ovaries showing a reduced trend in primordial follicles numbers in the mutant ovaries, which is not statistically different. (F) Double immunolabeling of SYCP3 and SYCP1 showing aberrant synapsis and structural abnormalities in the XY chromosome pair including X-autosome fusions (b), ring chromosomes (c), XY autosynapsis (d), and unpaired and autosynapsis (e). The quantitation numerical values of these aberrant configurations in the XY bivalent in Rnf212b−/−, Rnf212−/−, Rnf212b−/− Rnf212−/−(dKO), and wild-type spermatocytes (WT) are shown in the lower table. (G) Double immunolabeling of SYCP3 with RNF212 and with HEI10 showing absence of fluorescent foci in Rnf212b−/− in comparison with the wild-type controls. Bar in (E–G) 10 μm. All experiments have been carried out in at least three mice and 100 cells per mouse in (F), and 15 cells in (G).