Figure 1. Potential mechanisms underlying the interaction between brain barrier-resident innate lymphocytes and the cells in the brain parenchyma.
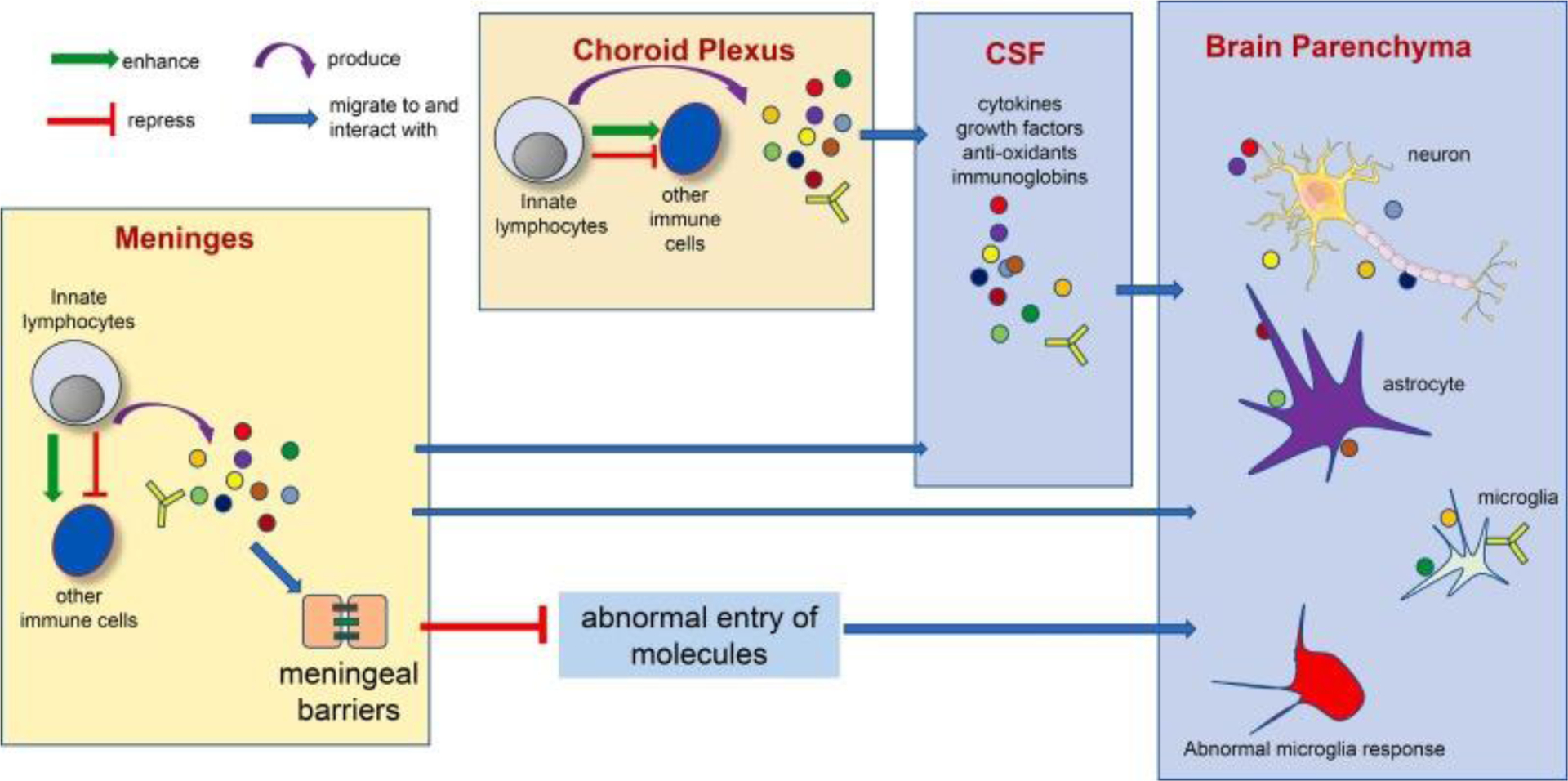
Multiple co-existing mechanisms might under the interaction between brain barrier-resident innate lymphocytes and the cells in the brain parenchyma. Innate lymphocytes at the brain barrier tissue may produce effector molecules that access cells in the brain parenchyma via CSF circulation. Innate lymphocytes may also stimulate or repress other immune cells to produce such effector molecules. Innate lymphocytes may also play an important role in regulating brain barrier integrity, thus preventing abnormal entry of undesirable molecules into the brain parenchyma and restricting neuroinflammation. Of note, the interaction between innate lymphocytes and the nervous system is bilateral. The nervous system may in turn control innate lymphocyte activity via various mechanisms (Yano and Artis 2022).
