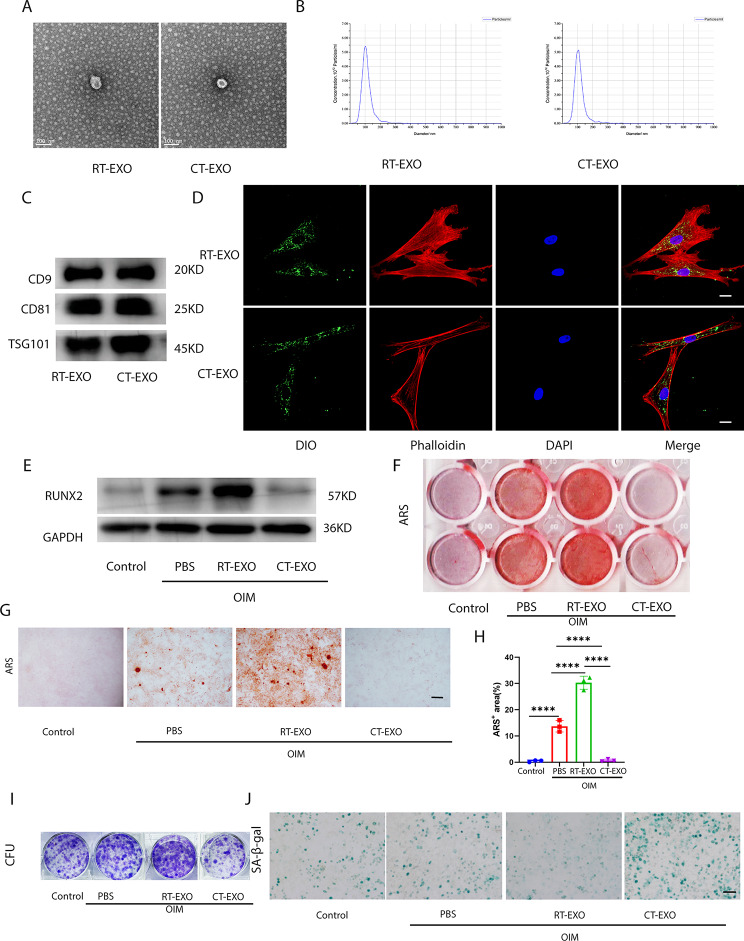
Fig. 4.
CT-EXO can be taken up by BMSCs and impair the osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs. A, Representative image of the ultrastructure of exosomes observed by transmission electron microscopy. Scale bar represents 100 μm. B, Average particle size distribution of exosomes. C, Exosomes markers CD9, CD81, and TSG101 determined by western blotting. D, Representative fluorescence micrograph of DiO-labelled exosomes (green) internalized by primary BMSCs, while blue represents the nucleus. The labelled exosomes were co-incubated with BMSCs for 12 h. Scale bar represents 20 μm. E, Representative western blot image showing the effect of CT-EXO on the protein levels of RUNX2 in BMSCs after 48 h co-incubation. F, G, Representative image of microscopic view (F) and entire plate view (G)ARS staining of BMSCs after exosomes treatment. Scale bars represents 250 μm. H, Quantification of the ARS. n = 3 per group. I, Representative image of colony formation assay after BMSCs were treated with exosomes. J, Representative image of SA-β-gal staining of BMSCs after exosomes treatment. Scale bar represents 100 μm. OIM represent the osteogenesis induced medium, and the Control represent the BMSCs without using the osteogenesis induced medium. * P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001, **** P < 0.0001