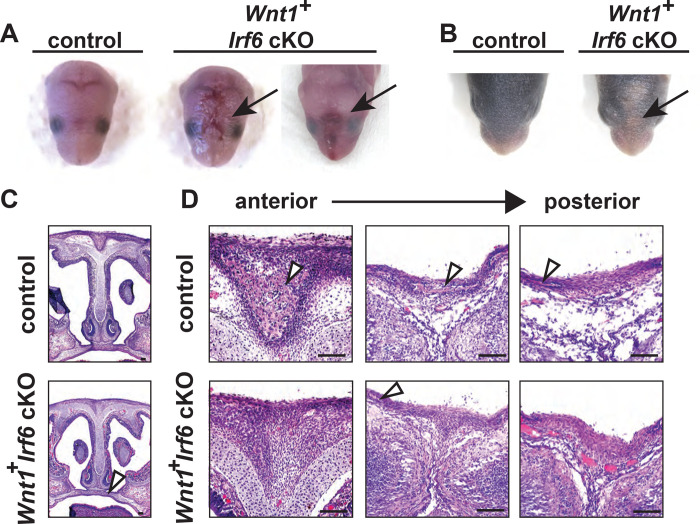
Fig. 3.
Wnt1-Cre-dependent Irf6 ablation causes cranial defects. A. Representative images of littermate control and Wnt1-Cre, Irf6 cKO pups at P0. At parturition, Wnt1-Cre+;Irf6fl/fl cKO mice display midline lesions of varying penetrance (arrow). B. Representative images of littermate control and Wnt1-Cre+;Irf6fl/fl cKO pups at P6. As the mouse neonate develops, these frontal lesions resolve but remain evident with deficient or delayed fur growth (arrow). C. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of coronal sections through the palate of E16 Wnt1-Cre+;Irf6fl/fl cKO and littermate control embryos shows normal development (arrow). D. Hematoxylin and eosin staining of coronal sections through the nasal and frontal bones of Wnt1-Cre+;Irf6fl/fl cKO and littermate control. Sections move anterior to posterior from left to right. Bone tissue is indicated with arrows. Wnt1-Cre+;Irf6fl/fl cKO mice have a lack of cranial bone development and suture formation at the midline (bone tissue indicated by arrows). Scale: 100 μM.