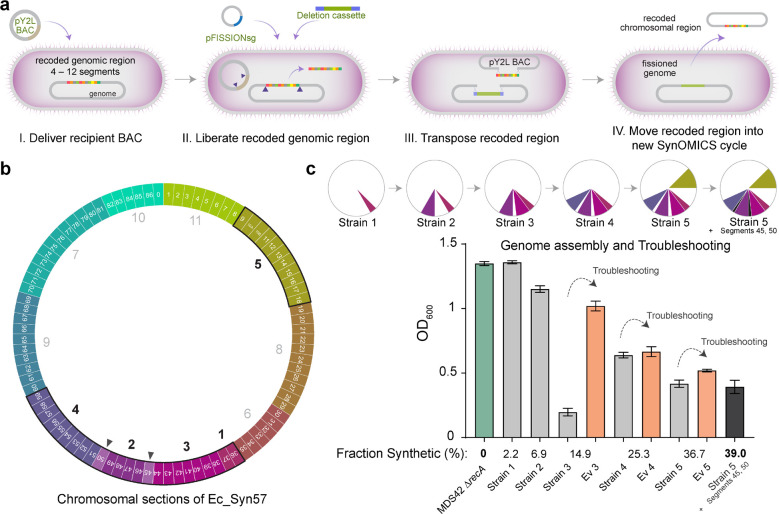
Figure 4. Assembly of recoded chromosomal regions to create Ec_Syn57.
(a) The reversal of SynOMICS’s steps and its direction allows genome fission, fusion, and assembly from separately constructed synthetic chromosomal regions. Chromosome fission is achieved by delivering recipient BAC (i.e., the pYES2L fission BAC, abbreviated as pY2L) into a cell line bearing a partially recoded chromosome (I.), and (II.) following the expression of Lambda-Red and Cas9 from pRedCas2 (not shown), chromosome fission is initiated by delivering pFISSIONsg—a four-plex nonrepetitive sgRNA expression plasmid—and a version of the SynOMICS deletion cassette that only contains terminal genomic homologies. (III.) CRISPR/Cas9-cuts liberate the recoded chromosomal region from the genome and linearize the recipient BAC allowing the Lambda-Red-mediated terminal homology-directed transposition of the recoded chromosomal region into the recipient BAC while simultaneously sealing the genomic cut. Finally, (IV.) the fissioned chromosomal region is delivered into a new recipient cell where it is integrated using the standard SynOMICS workflow, depicted on Figure 2c. (b) Construction of the synthetic genome of Ec_Syn57 from 11 simultaneously constructed synthetic sections. Numbers indicate the steps in which genomic sections are merged to assemble the final, fully synthetic genome of Ec_Syn57. Segments 45 and 50 (marked as ▲) were added following the merging of sections 1 to 5. To date, sections 1–5 have been combined, as indicated on Figure 4c, yielding 7 strains containing the synthetic genome of Ec_Syn57. (c) SynOMICS-based sequential assembly and troubleshooting of recoded chromosomal sections to generate Ec_Syn57. Following the construction of recoded chromosomal regions, we utilized SynOMICS (Figure 4a) to transfer and integrate recoded chromosomal regions in E. coli MDS42 ΔrecA containing Segments 36 and 37. Following the assembly of three chromosomal regions, we initiated genome-editing- and ALE-based troubleshooting to increase the fitness of partially recoded strains before the next chromosomal region was transferred. Pie chart displays the steps of genome assembly, colored sections mark synthetic recoded chromosomal regions transferred to obtain E. coli MDS42 ΔrecA containing Segments 9–18 and 36–59. For the detailed description of assembly steps, see Supplementary Methods. Bar graph shows final optical density at 600 nm (OD600) following aerobic growth in 2×YT broth, a rich bacterial growth medium, at 37 °C. Source data is available in this paper.