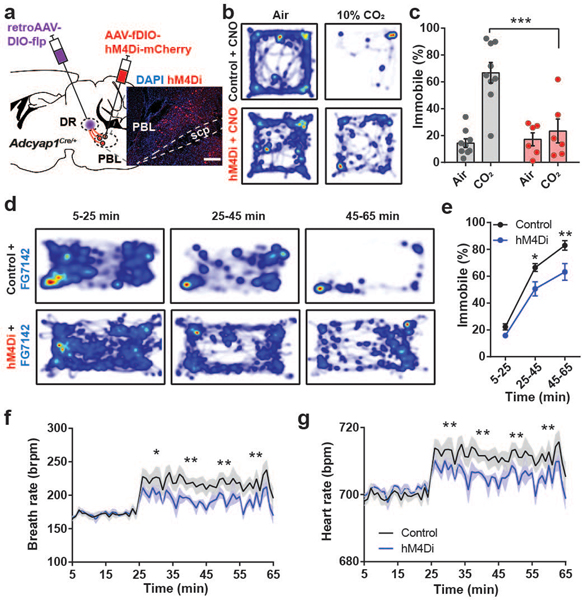
Fig. 5. Inhibition of PACAPPBL→DR neurons attenuates panic-like symptoms.
a, Schematic and histological confirmation of Cre- and Flp-dependent expression of hM4Di in the PBL of an Adcyap1Cre/+ mouse for chemogenetic inhibition of PACAPPBL→DR neurons. Scale bars: 100 µm. This experiment was repeated on six mice with similar results. b,c Representative heat maps of mouse activity (b), and immobile behavior (c, repeated measure two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test) before (normal air) and after CO2 exposure during chemogenetic inhibition of PACAPPBL→DR neurons. n = 9 control mice, n = 6 hM4Di mice. d,e, Representative heat maps of mouse activity (d), and immobile behavior (e, repeated measure two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test) after FG-7142 injection during chemogenetic inhibition of PACAPPBL→DR neurons. n = 9 control mice, n = 5 hM4Di mice. f,g, Breathing (f, repeated measure two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test), and heart rate (g, repeated measure two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s multiple comparisons test) changes after FG-7142 injection during chemogenetic inhibition of PACAPPBL→DR neurons. n = 9 control mice, n = 5 hM4Di mice. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM; see also Supplementary Table 3 for statistical details. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001.