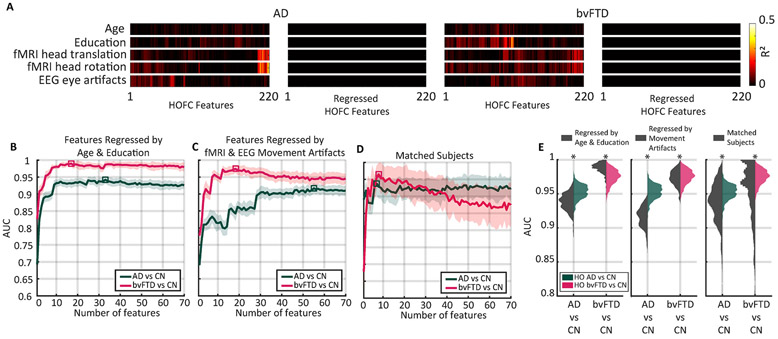
Fig. 5.
HOFC is robust against the linear influence of demographics and motor artifacts on HOFC. A) Variance of HOFC features (220 features) explained by age, education, fMRI head movements (translation and rotation), and EEG eye artifacts before and after multivariate linear regression. Colour scale is the R2 (square of the Pearson’s correlation coefficient). B) Classifiers’ performance using HOFC features where the effect of age and education was removed by multivariate linear regression. Solid lines and shaded areas represent the average and standard deviation, respectively. Squared denotes the maximal AUC obtained following the feature selection procedure. C) Same as B, but with features regressed by fMRI head artifacts and EEG eye artifacts. D) Classifier’s performance using raw HOFC features for a subsample of the population where age and education were matched (Table 2). E) Distributions of AUC values associated with the squares in B, C, and D. Sixty independent random splits were used for cross-validation. Asterisks denote Mann-Whitney p-value <10–6. bvFTD: behavioral variant of frontotemporal dementia; AD: Alzheimer’s disease; R2: coefficient of determination; CN: healthy controls group; HO: high-order; HOFC: high-order functional connectivity; AUC: Area under the receiver operating characteristic curve.