Table 1:
Examples of the use of biomarkers for understanding the effect of toxic environmental exposures.
| Exposure | Internal dose | Biologically effective dose | Early biologic effect | Alterations in structure and/or function | Disease | Prognosis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lead | Blood lead levels | Lead levels in the bone marrow cells | Inhibition of the D-aminolaevulinic acid dehydratase | Accumulation of Zn-protoporphyrin | Anaemia | Rate of lead decrease after cessation of the exposure |
| Fatty foods | Serum cholesterol | LDL/HDL | Blood diamicrons | Serum enzymes of myocardial necrosis | Atherosclerosis | Serum enzymes of myocardial necrosis |
| Ethylene dioxide | Haemoglobin adducts | DNA adducts | Hypoxanthine guanine phosphoribosyl transferase mutation | Sister chromatid exchange | Leukaemia | ? |
| Dioxin |
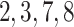 -tetrachloro- dibenzo-p-dioxin
-tetrachloro- dibenzo-p-dioxin |
Urinary porphyrins | Hyperkeratinization of sebaceous glands | ? | Chloracne | ? |
