Fig. 1. T cell-driven inflammation alters the intestinal BA pool.
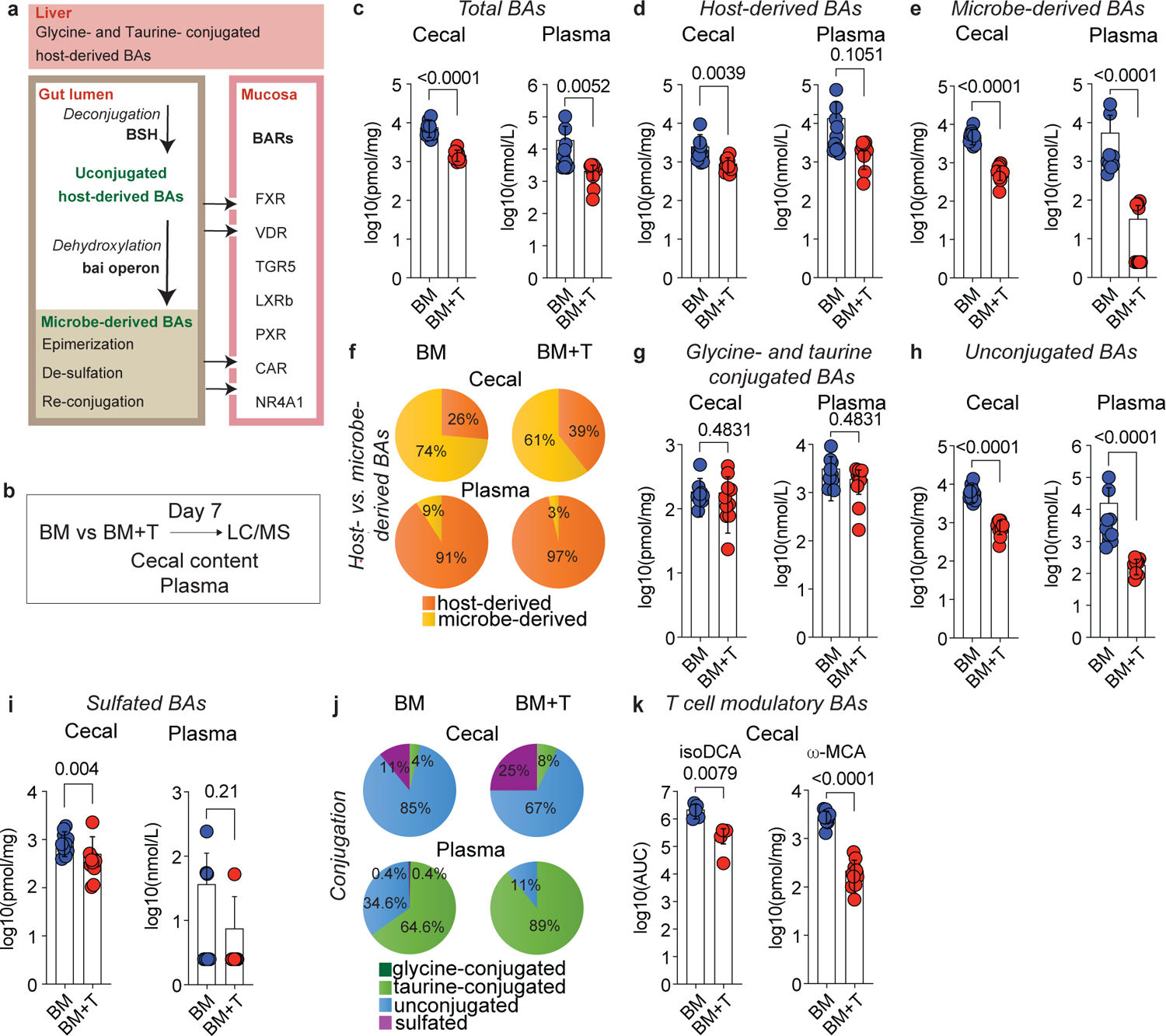
Lethally irradiated 6–8 week old female BALBc mice were transplanted with 10 × 106 BM cells alone (BM) or together with 1 × 106 T cells (BM+T). (a) Simplified schematic overview of BA metabolism. In humans, the host-derived BA pool is primarily composed of CA and CDCA, while in mice α- and β-MCA are dominant. Approximately 95% of the BAs are absorbed in the terminal ileum and enter the enterohepatic circulation, while the remaining 5% are transformed by gut bacteria into various microbe-derived BAs. BAs can bind to several BA receptors (BARs) including the Farnesoid X Receptor (FXR), the Vitamin D Receptor (VDR), the G protein-coupled BA Receptor 1 (TGR5), the Liver X Receptor β (LXRβ), the Pregnane X Receptor (PXR), the Constitutive Androstane Receptor (CAR), and the Nuclear Receptor 4A1 (NR4A1). (b) Experimental workflow for BA analyses during preclinical GVHD. (c-k) Analysis of cecal contents and plasma on day 7 by LC-MS. Concentration of total (c), host-derived (d), and microbe-derived BAs (e). Pie chart showing the relative abundances of host- and microbe-derived BAs (f). Concentration of glycine- and taurine-conjugated (g), unconjugated (h), and sulfated BAs (i). Pie chart showing the relative abundances of glycine- and taurine-conjugated, unconjugated, and sulfated BAs (j). Cecal levels of the T cell immunomodulatory BAs isoDCA and ω-MCA (k). (c-k) Data combined from two independent experiments (n=10) and shown as mean ± S.D or averaged percentages. IsoDCA levels in (k) are reported as AUCs and representative of two independent experiments (n=5). Statistical significance was determined by a two-tailed Mann Whitney test.
