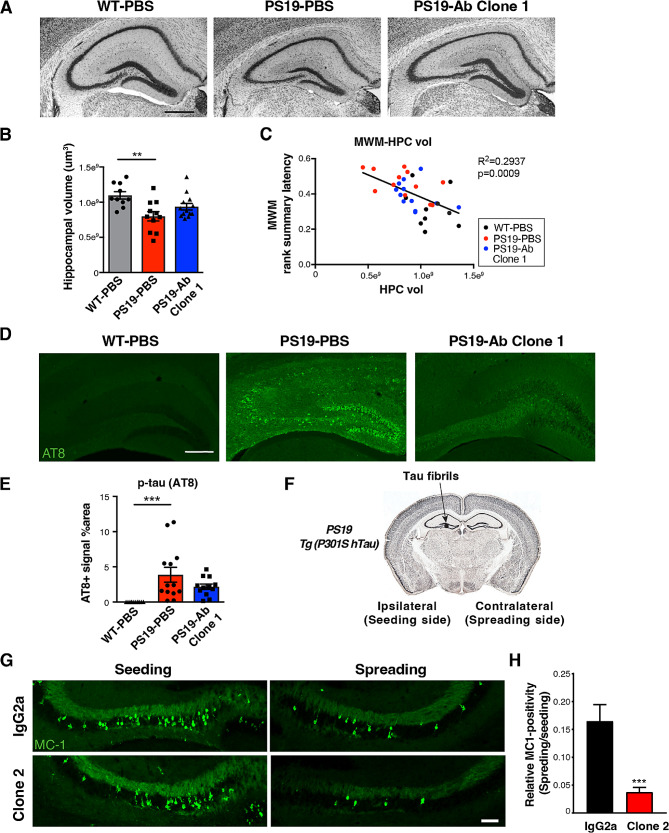
Fig. 3.
Anti-ac-tauK174 antibody ameliorates tau pathology and neurodegeneration in PS19 mice. (A) Representative Nissl-staining showing hippocampal morphology of WT mice treated with PBS, PS19 mice treated with PBS, and PS19 mice treated with Clone 1 antibody. Scale bar: 500 µm. (B) Quantification of hippocampal volume. **p<0.01 by one-way ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test. (C) Pearson correlation analysis of Morris water maze performance score (rank summary latency during learning) and hippocampal volume. (D) Representative immunohistochemistry staining of p-tau (AT8) in the hippocampi. Scale bar: 250 µm. (E) Quantification of hippocampal AT8-positive area. ***p<0.001 by one-way ANOVA, Kruskal-Wallis test. (F) Schematic diagram showing the injection of tau fibrils to the hippocampus of PS19 mice induces spreading of tau pathology from the ipsilateral (seeding) side to the contralateral (spreading) side of the brain. (G) Representative immunostaining showing MC1-positive tau inclusions in the seeding side and the spreading side after treatment with IgG2a or Clone 2 antibody. Scale bar: 100 µm. (H) Quantification of relative MC1-positive signal in IgG2a and Clone 2 treated groups, normalizing the spreading side to the seeding side. n = 5 mice for both groups. ***p<0.001, STATA mixed model