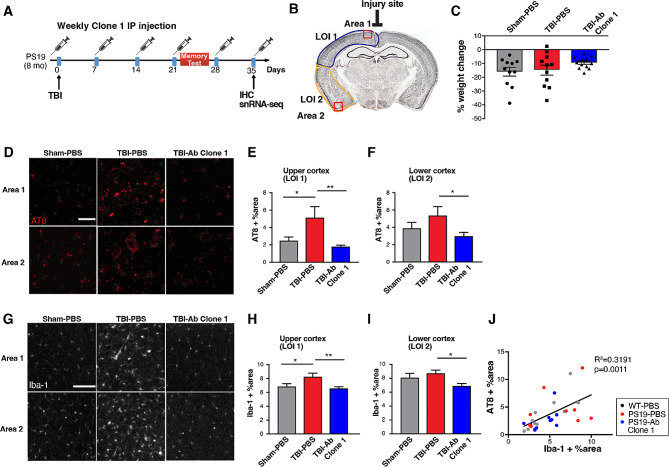
Fig. 4.
Anti-ac-tauK174 treatment ameliorates behavioral impairments and neuropathology in P301S mice with TBI. (A) 8-month PS19 mice were exposed to sham or traumatic brain injury (closed head concussive) surgery. One day prior to trauma surgery animals received PBS or Clone 1 administered intraperitoneally (IP). Treatment continued weekly throughout the duration of experimentation until termination 5 weeks post-injury. (B) Schematic diagram showing the injury site and areas of pathology analysis. (C) Percentage of weight loss at Day 28 among three groups of PS19 animals showing a trend of reduction in mice with TBI and treated with antibody. (D, G) Representative immunohistochemistry staining of AT8-positive p-tau (F) and Iba-1 (I) in the upper (LOI 1) and lower (LOI 2) cortex of PS19 mice with sham surgery or TBI, treated with PBS or Clone 1 antibody. Scale bar: 100 µm. (E, F, H, I) Quantification of AT8 positive % area (E, F) and Iba-1 positive % area (H, I) in upper and lower cortex of the three sections adjacent to the injury site. **p<0.01, *p<0.05 by one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparison test. (J) Pearson correlation analysis of AT8-positive p-tau levels (by western blot) and Iba-1 signal in the lower cortex. n = 12 per group