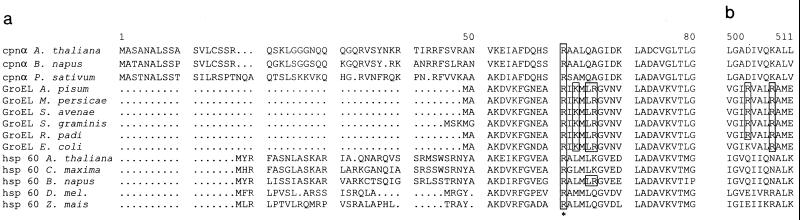
FIG. 9.
Alignment of Hsp60/GroEL amino acid sequences of mitochondria, E. coli, and chloroplasts. Shown are chloroplast cpn α (subunit of chloroplast Hsp60) of Arabidopsis thaliana (accession no. P21238), Brassica napus (P34794), and Pisum sativum (P08926); mitochondrial hsp60 of A. thaliana (P29197), Cucurbita maxima (Q05046), B. napus (P35480), Drosophila melanogaster (O02649), and Zea mais (P29185); Buchnera GroEL sequences of Acyrthosiphon pisum (P25750), M. persicae (AF003957), Schizaphis graminum (Q59177), Sitobion avenae (U77379), and Rhopalosiphum padi (U77380); and GroEL of E. coli (reference 14). Sequences were aligned using the PILEUP program (Genetics Computer Group, Madison, Wis. [8]). (a) Alignment of the first 80 amino acids of the N-terminal regions of GroEL/Hsp60 equatorial domains. (b) Alignment of amino acids 500 to 511 of the C-terminal regions of GroEL/Hsp60 equatorial domains. Amino acids shown to be involved in PLRV-binding are boxed. The highly conserved R13 is indicated by an asterisk.