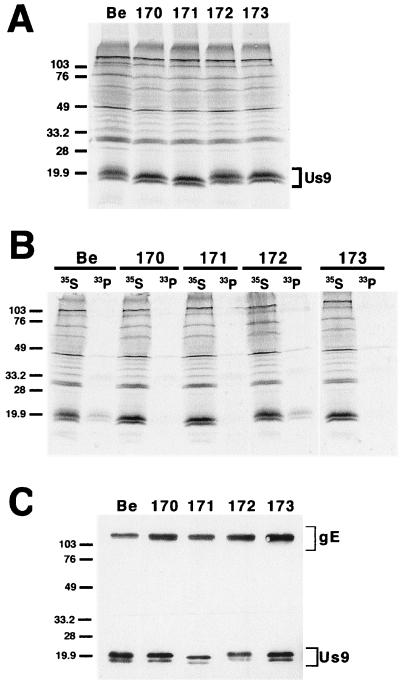
FIG. 5.
Analysis of the alanine scanning Us9 proteins. (A) Steady-state expression of alanine scanning Us9 proteins. PK15 cells infected with PRV Be (wild type), PRV 170 (Y49–50A S51A S53A), PRV 171 (E52A D54A N55A E56A), PRV 172 (Y49–50A), or PRV 173 (S51A S53A) were radiolabeled overnight with [35S]methionine-cysteine. Cellular extracts were prepared at 16 h postinfection and immunoprecipitated with Us9 polyvalent antiserum. (B) Analysis of Us9 phosphoforms. PRV Be (wild type)-, PRV 170 (Y49–50A S51A S53A)-, PRV 171 (E52A D54A N55A E56A)-, PRV 172 (Y49–50A)-, and PRV 173 (S51A S53A)-infected cells were radiolabeled overnight in the presence of either [35S]methionine-cysteine or [33P]orthophosphate. Cellular extracts were prepared at 16 h postinfection and subjected to immunoprecipitation with Us9 polyvalent antiserum. All of the immunoprecipitated products were analyzed by electrophoresis on an SDS–12.5% polyacrylamide gel followed by autoradiography (exposure time, 1.5 days). (C) Incorporation of Us9 into viral particles. Monolayers of PK15 cells were infected at an MOI of 10 with either PRV Be (wild type), PRV 170 (Y49–50A S51A S53A), PRV 171 (E52A D54A N55A E56A), PRV 172 (Y49–50A), or PRV 173 (S51A S53A) for 15 h. Cellular extracts were prepared, and virions were isolated from the medium by centrifugation through a 30% sucrose cushion. The purified virion extracts were fractionated on an SDS–12.5% polyacrylamide gel and analyzed by Western blotting with gE polyvalent and Us9 monoclonal (5F10) antisera. Molecular mass markers (kilodaltons) are indicated on the left in all three panels.