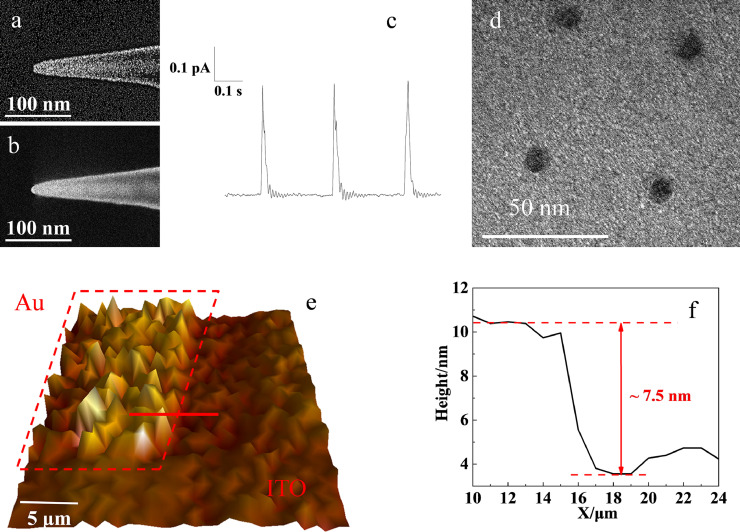
Fig 2.
(a), (b) SEM image of the nanocapillary with an opening of 20 nm (a) and the capillary filled with solid electrolyte exhibiting a nanoball at the tip (b); (c) the typical current trace recorded during the consecutive contacts by the nanoball at ITO surface; (d) SEM image of the Au layer after the contact with the nanoball and the electrochemical corrosion; (e) the SECCM image of Au layer at the ITO surface using the nanocapillary filled with the solid electrolyte; and (f) the height difference between Au layer and ITOs surface as marked with red line in Figure 2.