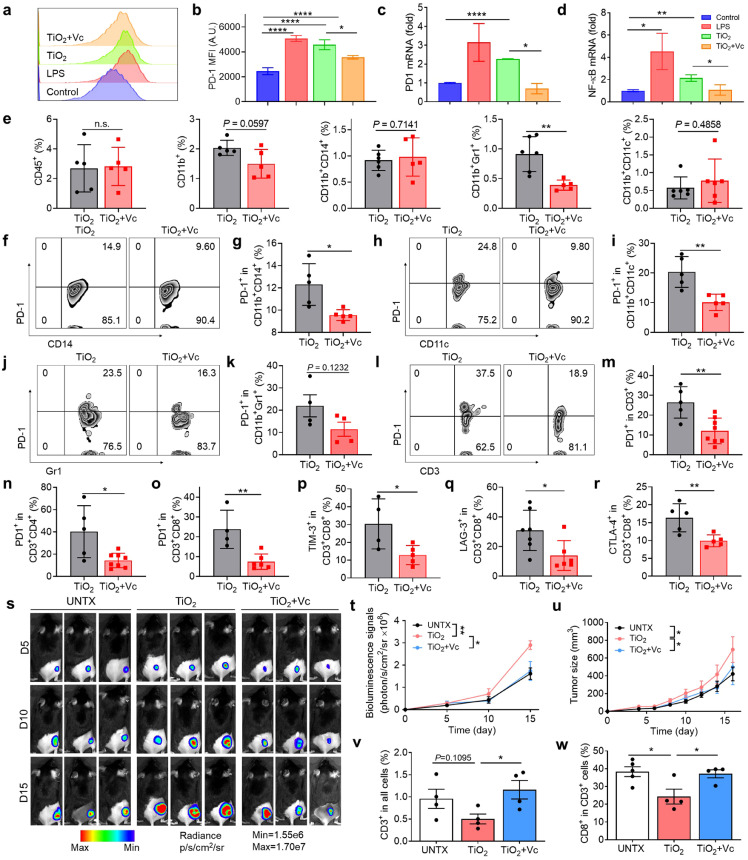
Fig. 5.
Vitamin C abolishes the immunosuppressive microenvironment induced by TiO2nanoparticles. (a) Flow cytometry chart of PD-1 and (b) quantitation of PD-1 in RAW 264.7 cells after treatments. (c) PCR analysis of PD-1 mRNA and (d) NF-κB mRNA expression. (e) Proportion of immune cells in tissues after vitamin C treatment, including leukocytes (CD45+), myeloid cells (CD11b+), monocytes/macrophages (CD11b+CD14+), MDSC (CD11b+Gr1+), and dendritic cells (CD11b+CD11c+). (f) Flow cytometry analysis and (g) quantitation of PD-1 in monocytes/macrophages in the tissue after vitamin C treatment. (h) Flow cytometry image and (i) quantitation of PD-1+ DCs. (j) Flow cytometry image and (k) of PD-1+ MDSCs. (l) Flow cytometry image and (m) quantitative analysis of PD-1+ T cells. (n) The proportion of PD-1 expression on CD3+CD4+ and (o) CD3+CD8+. (p) The proportion of TIM-3 expression on CD3+CD8+ T cells. (q) Quantitative analysis of LAG-3 expression on CD3+CD8+ T cells and (r) CTLA-4 expression on CD3+CD8+ T cells. (s) Representative bioluminescence images of the B16F10-Luc tumour after Vc treatment and (t) average radiance of tumours in mice. (u) The average tumour growth curves of mice receiving the indicated treatments. (v) The percent of CD3+ cells in the tumour and (w) the proportion of the CD8+ in CD3+ cells in the tumour. Values indicate mean ± SEM (n = 4–8). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.005, ****P<0.001 by Student`s t-test and one-way ANOVA using the Tukey post-test.