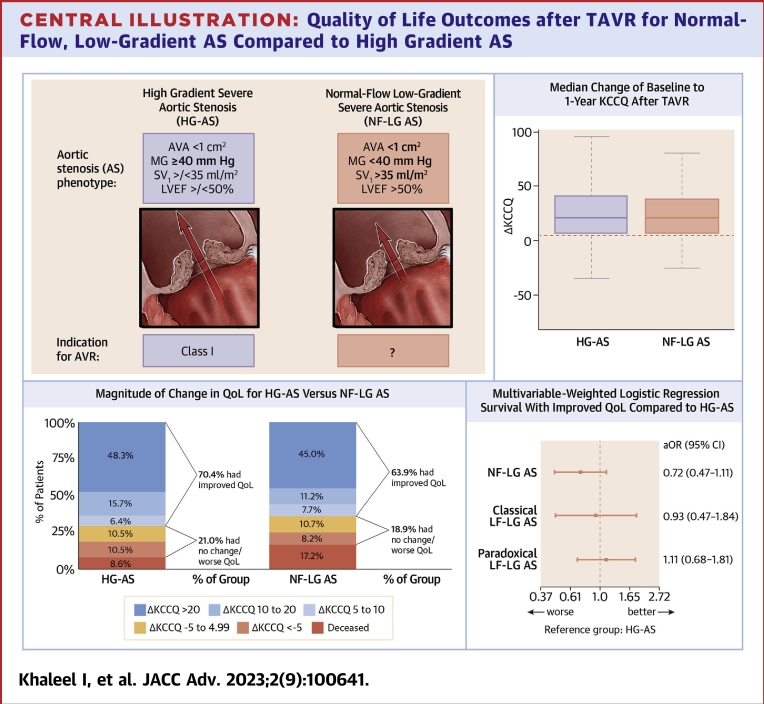
Central Illustration.
Quality of Life Outcomes after TAVR for Normal-Flow, Low-Gradient AS Compared to High Gradient AS
(Top left) Hemodynamic criteria for high-gradient severe aortic stenosis (HG-AS) and normal flow-low gradient severe aortic stenosis (NF-LG AS). AHA/ACC guidelines do not provide specific recommendations for timing of intervention for NF-LG AS. (Top right) Change in baseline to 1-year KCCQ shown only for patients alive with KCCQ follow-up for HG-AS and NF-LG AS groups. Boxes represent median with inner quartile range with whiskers representing 95% confidence intervals. (Bottom left) Magnitude of baseline to 1-year KCCQ change in patients with complete follow-up (mortality or KCCQ follow-up data) comparing HG-AS and NF-LG AS Groups. (Bottom right) Primary adjusted end point consisting of: 1) survival to 1 year; and 2) improved KCCQ score of ≥5 for AS groups compared to HG-AS group as reference. aOR = adjusted odds ratio; AV = aortic valve; AVA = aortic valve area; AVR = aortic valve replacement; KCCQ = Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire; LF-LG = low-flow, low-gradient; LVEF = left ventricular ejection fraction; MG = mean gradient; SVi = indexed stroke volume; TAVR = transcatheter aortic valve replacement.