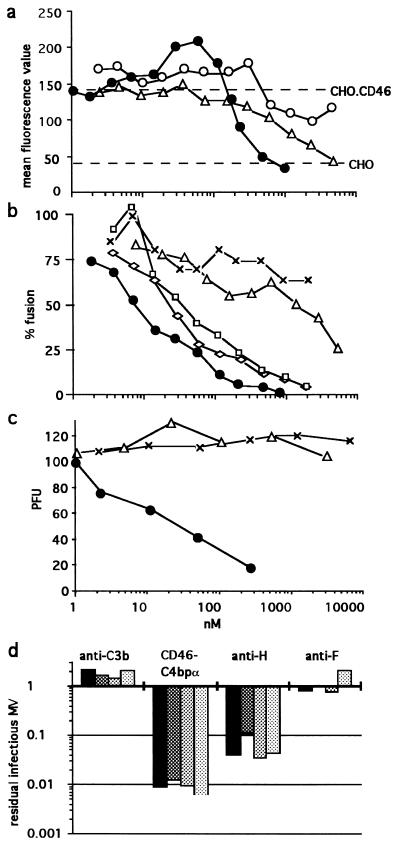
FIG. 3.
Inhibition of virus binding (a), virus-induced cell-cell fusion (b), and virus infectivity (c and d). (a) Purified MV was incubated with either sCD46-C4bpα protein (black circles) or sCD46 protein (triangles) before the addition of CHO-CD46 cells; alternatively MV was incubated with CHO-CD46 cells to which the sCD46-C4bpα protein was added afterwards (open circles). (b) Inhibition of fusion in the presence of sCD46-C4bpα protein (circles), sCD46 protein (triangles), 48Cl6 anti-H (diamonds), Y503 anti-F (squares), or WM1 anti-C3b(C3c) (exes) MAbs. The results are expressed as a percentage of the fusion between HeLa and MV-infected HeLa cells observed in the absence of inhibitor as determined by the level of β-Gal activity. (c) MV (100 PFU) was incubated with sCD46-C4bpα protein (circles), sCD46 protein (triangles), or bovine serum albumin (exes) prior to infection of Vero cells. (d) MV (105, 104, 103, and 102 TCID50 [black to light grey columns, respectively]) was incubated with the indicated reagent, and the remaining virus was titrated using the TCID50 assay. The results are expressed as the MV fraction not neutralized. Note that no infectious MV was recovered from 102 TCID50 MV incubated with sCD46-C4bpα (i.e., recovery fraction = 0:100).