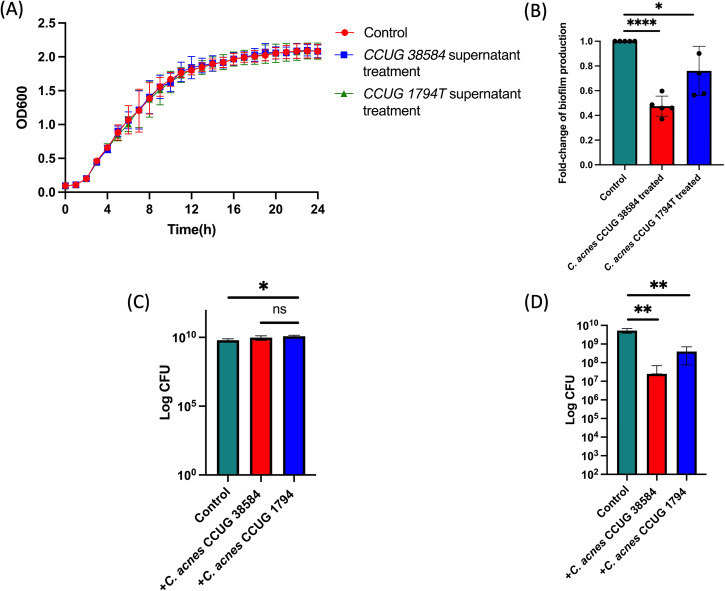
Fig. 2. Impact of C. acnes on P. aeruginosa growth and biofilm formation.
A Growth curve of P. aeruginosa PA14 liquid cultures in the presence of C. acnes strains supernatants (50%) showing no significant difference in the growth rates between exposures. Two-way ANOVA with multiple comparisons was performed to assess statistical significance. P value > 0.05 was determined as insignificant (ns). B The effect on biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa PA14 in the presence of C. acnes strains supernatants after 24 h. C. acnes CCUG 38584 supernatant treatment exhibited a 52.5% reduction of the biofilm production in P. aeruginosa PA14, whereas C. acnes CCUG 1794T exhibited a less significant 24% reduction in comparison to the control treatment. Unpaired Student’s t test (two tailed) was performed to assess statistical significance. ****p value < 0.0001, *p value < 0.05. Error Bars are Standard Deviation. C Growth of P. aeruginosa PA14 in an artificial sebum model in the presence of C. acnes CCUG 1794T and CCUG 38584 cultures. No negative effects on growth were observed. Unpaired Student’s t test (two tailed) was performed to assess statistical significance *p value < 0.05. Error Bars are Standard Deviation. D Biofilm formation of P. aeruginosa PA14 in an artificial sebum model in the presence of C. acnes CCUG 1794T and CCUG 38584 cultures after 48 h. Unpaired Student’s t test (two tailed) was performed to assess statistical significance **p value < 0.01. Error Bars are Standard Deviation.