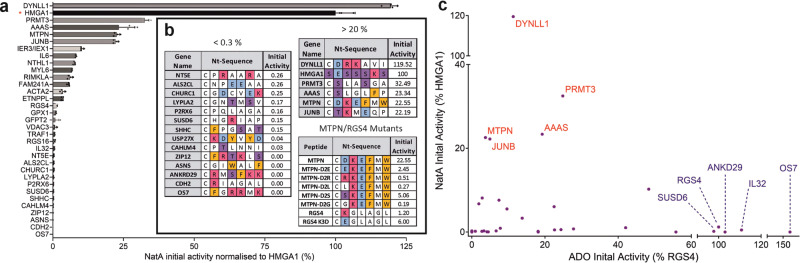
Fig. 6. Investigation of NatA-catalysed acetylation of Nt-Cys sequences.
a [14C]-Acetyl incorporation into CX6RWGRPVGRRRRPVRVYP peptides (where CX6 is the 1st 7 amino acids of the Met-excised N-terminal sequence of protein of interest) after 5 min (200 µM peptide, 0.3 µM NatA, 200 µM Ac-CoA, 37 °C); activity is normalised to [14C]Acetyl incorporation into SESSSKSRWGRPVGRRRRPVRVYP (HMGA1) positive control peptide in the same assay (indicated with *). Data represent mean ± standard deviation; n = 4. b N-terminal sequences of peptides with which NatA was observed to have < 0.3% or > 20% activity compared to HMGA1 positive control peptide. MTPN peptide mutants varying the identity of the amino acid following the Nt-Cys were designed and tested (as in a) as well as RGS4 K3D. Amino acids are colour coded according to chemical properties: basic (H/K/R) = red; acidic (D/E) = blue; aromatic (F/W) = orange; polar (S/T) = purple. c Activity of NatA (a) plotted against activity of ADO (Fig. 2a) for Nt-Cys proteins of interest. Names of best NatA substrate peptides shown in red and names of best ADO substrate peptides shown in blue. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.