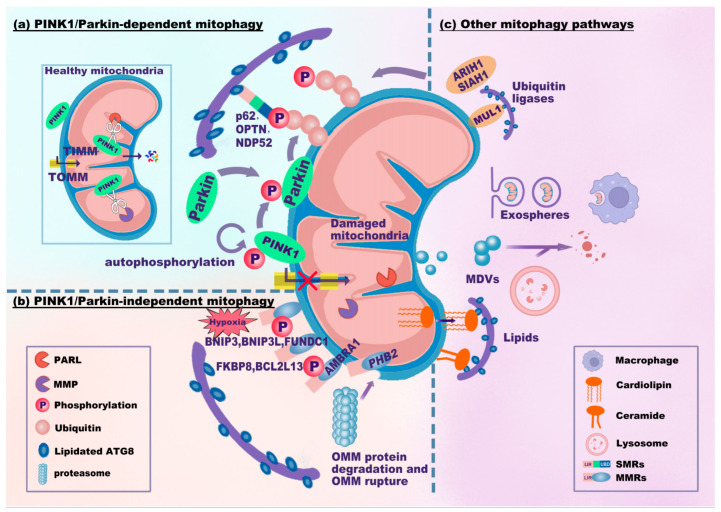
Figure 2.
Mitophagy signaling pathways. The mitophagy signaling pathways can be classified as PINK1/Parkin-dependent (a), PINK1/Parkin-independent (b), or other mitophagy signaling pathways (c). (a) In healthy mitochondria, PINK1 translocates into mitochondria through TOMM and TIMM and is proteolytically cleaved by PARL and MPP. Upon mitochondrial damage, PINK1 fails to enter and accumulates on the OMM, which recruits and phosphorylates Parkin. PINK1 and Parkin jointly generate p-Ub chains on the OMM. SMRs (e.g., p62, OPTN, and NDP52) recognize p-Ub signals and link damaged mitochondria to phagophores via the LIR-ATG8 interaction. (b) MMRs directly interact with lipidated ATG8. BNIP3, BNIP3L, and FUNDC1 are common in response to hypoxia. PHB2 localizes to the IMM. Upon proteasome-mediated rupture of the OMM, PHB2 interacts with ATG8. (c) Several ubiquitin ligases, MUL1, SIAH1, and ARIH1, ubiquitinate the OMM to promote mitophagy. Notably, MUL1 has an LIR motif that interacts with ATG8. Damaged mitochondria can be translocated to other cells (e.g., macrophages) through exospheres or EVs for mitophagy. MDVs derived from mitochondria fuse with lysosomes for degradation. Cardiolipin translocates from the IMM to the OMM to interact with ATG8. Abbreviations: TOMM/TIMM, translocase complex of the outer/inner mitochondrial membrane (OMM/IMM); PARL, presenilin-associated rhomboid-like protein; MPP, mitochondrial processing peptidase; p-Ub, phosphorylated ubiquitin; MDVs, mitochondria-derived vesicles; EVs, extracellular vesicles.