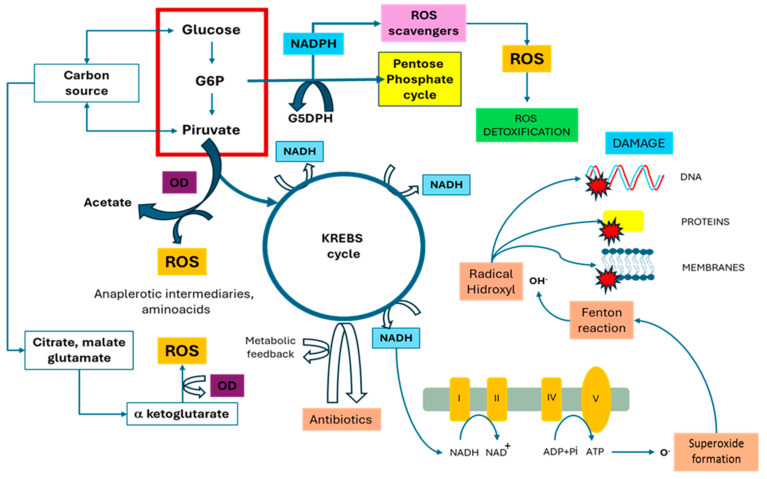
Figure 1.
The image shows that the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) occurs through the primary metabolism and the adjuvant phenomenon in the presence of antibiotics. This can lead to an increase in the concentration of ROS and cellular damage to nucleic acids, membranes, and proteins. The Roman numerals represent the domains of the electron transport chain where reactive oxy-gen species are produced (OD) Oxidative decarboxylation; (NADPH) nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate; (G6P) glucose 6 phosphate; (G5DP) glucose 5 diphosphate.