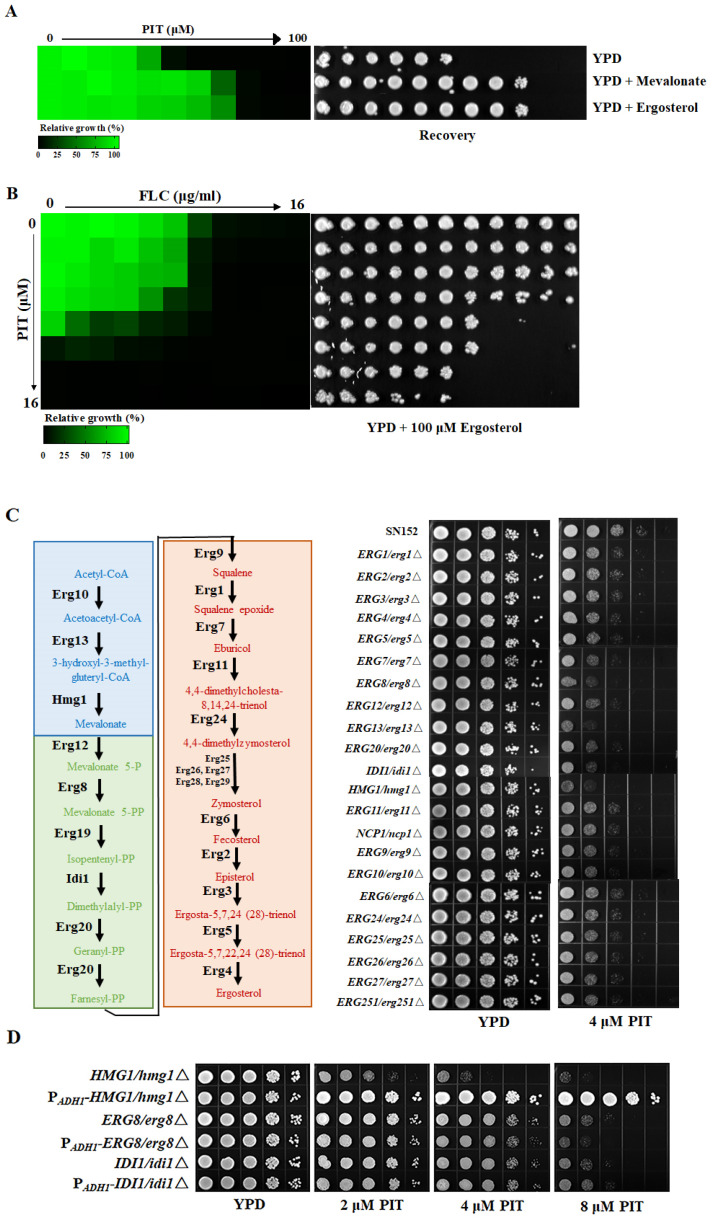
Figure 6.
(A) MIC assays and spotting assays show that feeding 100 μM exogenous (RS)-mevalonate lithium or ergosterol could counteract the antifungal activity of PIT in C. albicans SN152. (B) Dose–matrix titration assays indicated that 100 μM ergosterol counteracted the antifungal activity of FLC and PIT. (C) (Left) The diagrammatic sketch of ergosterol biosynthesis pathway in C. albicans. The different colored boxes represent the three modules: the mevalonate pathway is the blue box; the green box is composed of farnesyl pyrophosphate biosynthesis; and the final orange box contains ergosterol biosynthesis. (Right) Compared to the SN152 strain and other heterozygous gene deletion mutants, the HMG1/hmg1Δ, ERG8/erg8Δ, and IDI1/idi1Δ mutants are more susceptible to 4 μM PIT. (D) Spotting assays were performed on the solid YPD medium containing different concentrations of PIT (0, 2, 4, and 8 μM). Only over-expressed HMG1 gene could counteract the antifungal activity of PIT, rather than the ERG8 and the IDI1 genes.