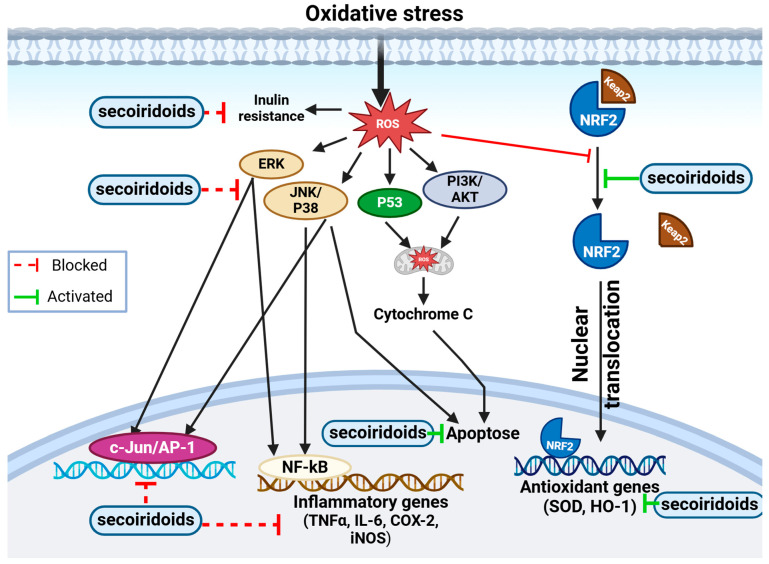
Figure 7.
Figure illustrating the molecular representation of the antioxidant mechanism of secoiridoids. This potent antioxidant has the potential to mitigate intracellular ROS levels. ROS, known to induce inflammation via NF-kB and AP-1 activation, trigger various cellular signaling processes leading to the production of inflammatory mediators. Secoiridoids effectively block these mediators. Additionally, secoiridoids might regulate cellular signaling by impacting signal transduction pathways. They demonstrate protective properties by activating the PI3-kinase/Akt pathway, stimulating MAPK proteins (ERK, JNK, and P38), and facilitating Nrf2 translocation into the nucleus. Furthermore, secoiridoids elevate the expression of MnSOD and HO-1, providing defense against oxidative stress through the Nrf2 pathway.