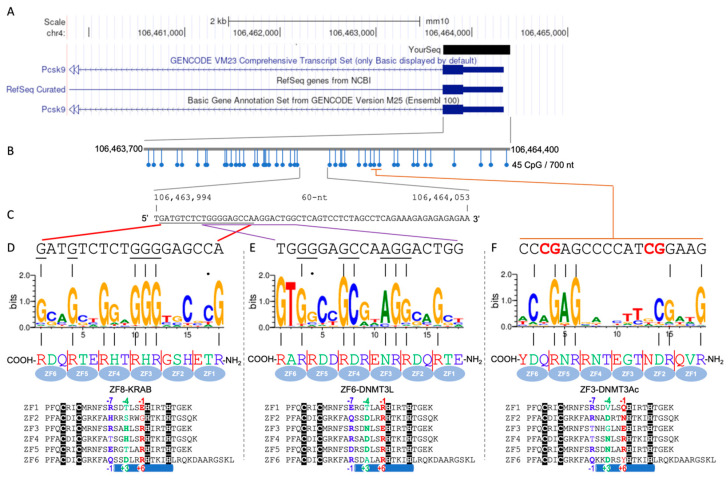
Figure 1.
CpG island of mouse Pcsk9 targeted by three ZF fusion proteins. (A) Mouse Pcsk9 is located on chromosome 4 (mm10). (B) The 700 nt CGI that spans the promoter region of Pcsk9 contains 45 CpG dinucleotides. (C) There is a CpG-free 60 nt gap within the CGI. (D–F) The 18 bp DNA elements potentially occupied by the fusion proteins ZF8-KRAB (D), ZF6-DNMT3L (E), and ZF3-DNMT3Ac (F). Top line: the actual 18 bp DNA sequence from 5′ to 3′ (left to right). Second line: sequence logo generated using a random forest (RF) prediction model [15], with regression on a bacterial one-hybrid system (B1H) [16,17,18]; the matched purines between the actual and the predicted DNA-binding sequences are indicated by vertical lines. Third line: the three base-interacting residues at −7, −4, and −1 of each finger from the NH2-to-COOH termini (right-to-left). The bottom section shows all six ZF motifs from each fusion protein sequence, taken from supplementary information Table 6 of [10]. The matching text colors in the third line and bottom section highlight the key recognition residues at positions −1, −4, and −7 of each finger as indicated. Note: this sequence-based numbering (−1, −4, and −7), relative to the first Zn-associated histidine, corresponds to the structure-based numbering of +6, +3, and −1 (relative to the start of the α-helix) [19].