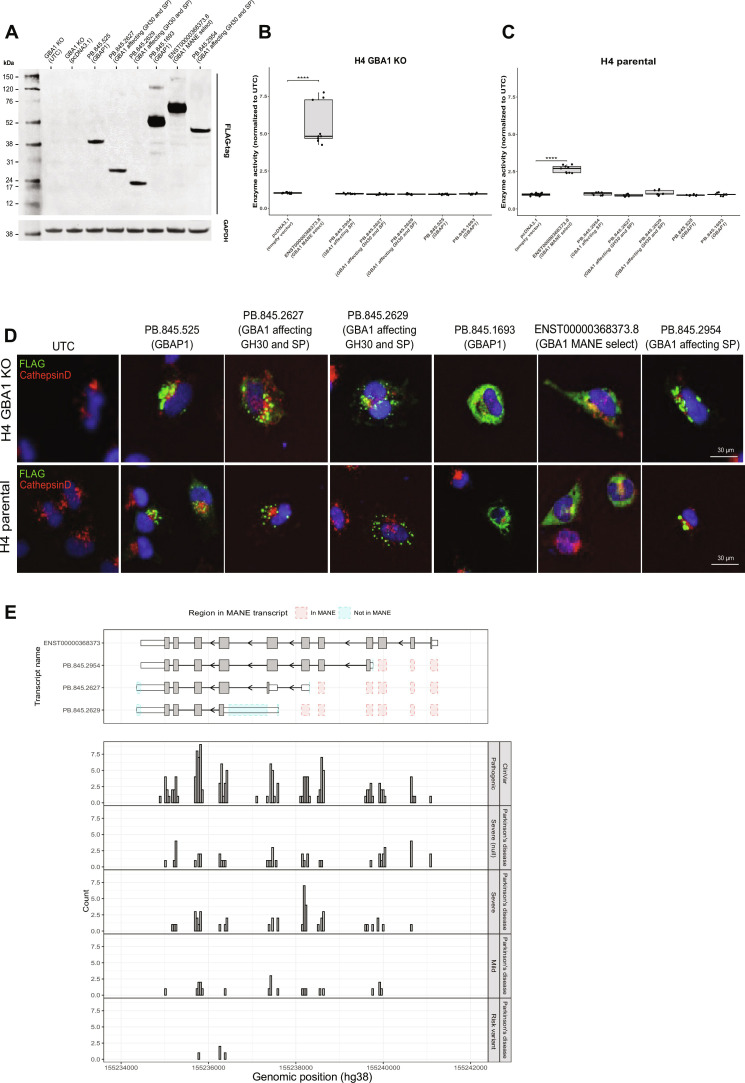
Fig. 6. Novel GBA1 and GBAP1 transcripts are translated with no GCase activity and impaired lysosomal colocalization with implications for variant interpretation.
(A) Immunoblot of H4 GBA1(−/−/−) knockout cells transiently transfected with GBA1 and GBAP1 constructs containing a C-terminal FLAG-tag. GBA1 and GBAP1 expression was detected using FLAG-tag antibody. GAPDH was used as a loading control. The predicted protein sizes are as follows: PB.845.525 (GBAP1; 321 amino acids; 35 kDa), PB.845.2627 (GBA1 affecting GH30 and SP; 219 amino acids; 24 kDa), PB.845.2629 (GBA1 affecting GH30 and SP; 164 amino acids; 18 kDa), PB.845.1693 (GBAP1; 399 amino acids; 44 kDa), ENST00000368373 (GBA1 MANE select; 537 amino acids; 62 kDa), and PB.845.2954 (GBA1 affecting GH30 and SP; 414 amino acids; 46 kDa). (B) Lysosomal enzyme assay of H4 GBA(−/−/−) knockout cells transiently transfected with GBA1 and GBAP1 constructs (C) and in H4 parental. GCase enzyme activity was significantly increased only in H4 parental and GBA(−/−/−) knockout cells transiently transfected with the GBA1 full-length construct (ENST00000368373), compared to the empty vector control (n = 3). (D) Lysosomal colocalization is impaired in novel GBA1 and GBAP1 transcripts. Immunohistochemistry of H4 parental and GBA1(−/−/−) knockout (KO) cells transiently transfected with GBA1 and GBAP1 constructs containing a C-terminal FLAG-tag. Colocalization of GBA1-FLAG and GBAP1-FLAG (green) with CathepsinD (red) was detected using FLAG-tag antibody. (E) Pathogenic GBA1 variants from ClinVar and risk variants from the GBA1-PD browser, which include variants described in PD, annotated onto novel coding GBA1 transcripts plotted using ggtranscript with differences as compared to MANE select (ENST00000368373) highlighted in blue and red.