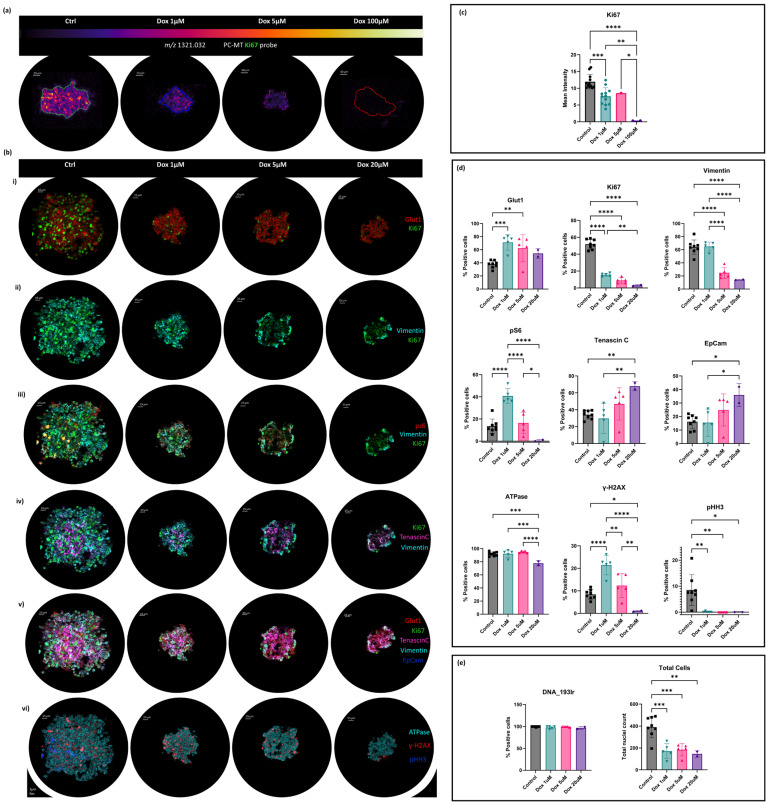
Figure 4.
(a) MALDI-IHC of SAOS-2 Multicellular Tumour Spheroids following 48 h of exposure to the following doxorubicin doses: control, 1 μM, 5 μM, and 100 μM. Spheroids were stained with photocleavable mass tag antibodies for Ki67. The mass reporter m/z 1321.032 was detected in positive ionisation mode at 10 μm spatial resolution using the Rapiflex reflector TOF MS (Bruker Daltonics, Bremen, Germany). (b) Subcellular protein localisation IMC of SAOS-2 MCTSs following 48 h exposure to doxorubicin doses. Control and 1 μM, 5 μM, and 20 μM Dox-treated models were subjected to IMCyTOF MS following metal-tagged antibody staining and acquisition at 1 μm spatial resolution by the Hyperion Imaging System (Standard BioTools). Image overlays are presented for (i,ii) Glut1 and Ki67; (iii) ps6, Vimentin, and Ki67; (iv) Ki67, Tenascin-C, and Vimentin; (v) Glut1, Ki67, Tenascin-C, Vimentin, and EpCam; and (vi) ATPase, γ-H2AX, and pHH3. (c) Mean intensities of corresponding ions of interest are presented. p values obtained following one-way ANOVA are presented for comparisons between control and doxorubicin-treated MCTSs. (d) Percentages of positive cells for each protein marker are presented. p values obtained following one-way ANOVA are presented for comparisons between control and doxorubicin-treated MCTSs (e) Percentages of positive cells for DNA and total cell counts across all treatment groups are presented. p values obtained following one-way ANOVA are presented for comparisons between control and doxorubicin-treated MCTSs; p values = 0.1234 (ns), 0.0332 (*), 0.0021 (**), 0.0002 (***), and 0.0001 (****) calculated at a 95% confidence interval.