Table 1.
Complete Stereochemistry and Functions of E and D-series Resolvins, Protectins, and Maresins.
| Resolvin | Structure and Complete Stereochemistry |
Function |
|---|---|---|
| Resolvin E1 (RvE1) |
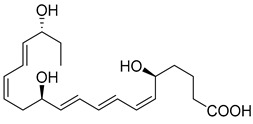 5S,12R,18R-trihydroxy-6Z,8E,10E,14Z,16E-EPA |
-Enhances macrophage phagocytosis of zymosan, E. coli, and apoptotic neutrophils [42]. -Reduces excessive neutrophil infiltration in murine models [42]. -Clears infections and stimulates resolution agonists in various diseases [43]. -Reduces depression in mice [44,45]. -Stops PMN [3] and dendritic cell migration [46]. -Inhibits TRP Channels [47]. -Modulates T-cell response [47]. -Inhibits platelet aggregation [48]. -Reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines [49]. Cancer: -Prevents liver injury and cancer cell transformation in hepatocellular carcinoma cells [50]. -Inhibits tumor growth in lung, pancreatic, and prostate cancers [31,51,52]. |
| Resolvin E2 (RvE2) |
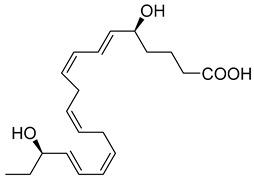 5S,18R-dihydroxy-6E,8Z,11Z,14Z,16E-EPA |
-Stops neutrophil chemotaxis to IL-8 and stimulates membrane shape changes in microfluidic chamber [53]. -Decreases depression in mice [45]. -Stops PMN migration [42,54]. -Down-regulates leukocyte integrins [53]. |
| Resolvin E3 (RvE3) |
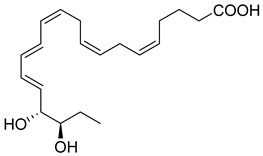 17R,18R-dihydroxy-5Z,8Z,11Z,13E,15E-EPA |
-Blocks neutrophil migration to the site of injury [55]. -Reduces allergic airway inflammation in house dust mice by down-regulating IL-23 and IL-17 [56]. -Decreases depression in mice [57]. |
| Resolvin E4 (RvE4) |
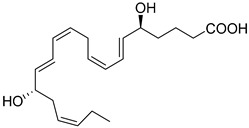 5S,15S-dihydroxy- 6E,8Z,11Z,13E,17Z-EPA |
-Stimulates macrophage efferocytosis of apoptotic neutrophils in senescent blood cells [58,59]. -Accelerated resolution of hemorrhagic exudates in vivo in mice [58]. |
| Resolvin D1 (RvD1) |
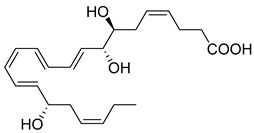 7S,8R,17S-trihydroxy-4Z,9E,11E,13Z,15E,19Z-DHA |
-Stop neutrophil infiltration and transmigration to the site of inflammation [60]. -Reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [60]. -Accelerates macrophage efferocytosis [1]. -In mice, prevents neutrophil recruitment, extravasation, and swarming that protect lungs from ischemia perfusion injury after transplantation [7]. -Inhibits TRP channels [61]. -Modulates T cell response [62]. -Reduces IgE production in mast cells [25]. Cancer: -Increases human monocyte-derived macrophages efferocytosis of cellular debris from chemotherapy-induced tumor cells and reduces the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines [63,64]. - Inhibits tumor growth in lung, pancreatic, and prostate cancers [31,51,52]. -Suppresses TAMs and enhanced tumor cell debris [65]. |
| Resolvin D2 (RvD2) |
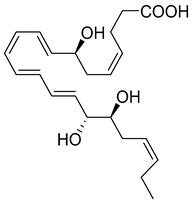 7S,16R,17S-trihydroxy-4Z,8E,10Z,12E,14E,19Z-DHA |
-Stops neutrophil infiltration and transmigration to the site of inflammation [66]. -Reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [66]. -Accelerates macrophage efferocytosis [66,67]. -Controls hepatic steatosis and fibrosis mediated by increasing infiltration of reparative M2 macrophages and protection of reparative monocytes in the bone marrow [68]. -Inhibits TRP channels [47]. -Modulates T cell response [62]. -Suppresses NLRP3 inflammasome by promoting autophagy in macrophages [69]. Cancer: -Increases human monocyte-derived macrophages efferocytosis of cellular debris from chemotherapy-induced tumor cells and reduces the secretion of pro-inflammatory cytokines [63,64]. -Reduces metastases in tumor-bearing mice of lung, liver, and pancreatic cancers [52]. -Shows in vitro and in vivo dose-dependent anti-tumor effects in oral squamous cell carcinoma [70]. -Suppresses TAMs and enhances tumor cell debris [65]. |
| Resolvin D3 (RvD3) |
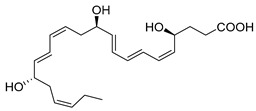 4S,11R,17S-trihydroxy-5Z,7E,9E,13Z,15E, 19Z-DHA |
-Blocks PMN migration [71]. -Reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines [72]. -Accelerates macrophage efferocytosis [71,72]-Restores epithelial barrier and function [71] Cancer: -Reduces metastases in tumor-bearing mice of lung, liver, and pancreatic cancers [52]. |
| Resolvin D4 (RvD4) |
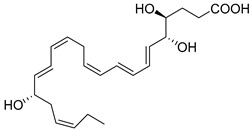 4S,5R,17S-trihydroxy-6E,8E,10Z,13Z,15E,19Z-DHA |
-Controls neutrophil deployment from bone marrow after emergency granulopoiesis initiated by E. coli peritonitis [26]. -Enhances fibroblast phagocytosis [73]. -Enhance thrombosis clearance and decreases neutrophil extracellular traps [74]. Cancer: -Reduces metastases in tumor-bearing mice of lung, liver, and pancreatic cancers [52]. |
| Resolvin D5 (RvD5) |
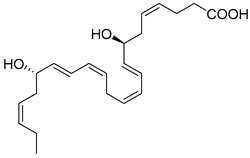 7S,17S-dihydroxy-4Z,8E,10Z,13Z,15E,19Z-DHA |
-Enhances bacterial clearance [75]. -Accelerates macrophage efferocytosis [75]. -Elevated in patients taking n-3 PUFA supplements via TPN [76]. -Plays a critical role in host defense and reduces arthritis by acting on T cells [77]. |
|
Protectin/
NeuroProtectin 1 (PD/NPD1) |
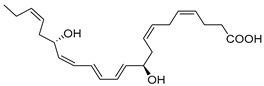 10R,17S-dihydroxy-4Z,7Z,11E,13E,15E,19Z-EPA |
-Defends the host from viral infection and bacteria by killing and clearing microbes [38]. -Significantly reduces infiltration of neutrophils and pathogenic CD4+ T cells in HSV-induced SK [78]. -Induces macrophage polarization switch towards non-inflammation in Zebrafish larva fin fold regeneration [79]. -Decreases post-infection lung eosinophils in vivo in models of RSV [80]. -Decreases polymorphonucler leukocyte recruitment and chemokine, cytokine levels in IRI [81]. -Elevated in patients taking n-3 PUFA supplements via total parenteral nutrition (TPN) [76]. |
|
Maresin 1
(MaR1) |
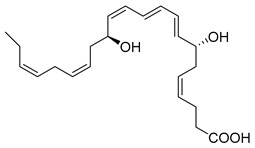 7R,14S-dihydroxy-4Z,8E,10E,12Z,16Z,19Z-DHA |
-Negatively correlated with depression severity in medication-naïve adolescents with first-episode major depressive disorder [82]. -Exogenous MaR1-LGR6 axis decreases IL-13 production in FoxP3-expressing regulatory T cells [41]. -In ALI, accelerates the resolution of inflammation by attenuating neutrophil accumulation and pulmonary edema [83]. -Intratracheal injection of MaR1, in high doses, increases in pro-inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and neutrophil infiltration in lung tissue [84]. -Attenuates hepatocyte apoptosis, ROS, and histopathological damage in macrophages [85]. -Elevated in patients taking n-3 PUFA supplements via TPN [76]. Cancer: -Reduces UVB-induced skin edema, neutrophil recruitment, cytokine production, and mast cells count in skin cancer [30]. |
|
Maresin 2
(MaR2) |
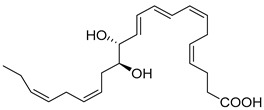 13R,14S-dihydroxy-4Z,7Z,9E,11E,16Z,19Z-DHA |
-Reduces neutrophil infiltration in mouse peritonitis and enhances human macrophage phagocytosis of zymosan [86]. -Exogenous MaR2 promotes mucosal repair following dextran sulfate sodium-induced colitis [87]. -Modulates monocyte/macrophage populations in the liver of DIO mice [88]. -Elevated in patients taking n-3 PUFA supplements via TPN [76]. |
