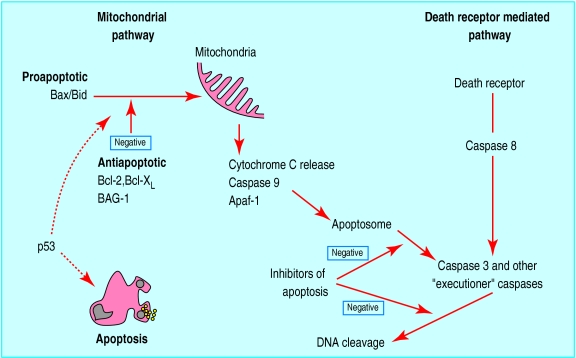
Figure 4.
Relation between some major controlling factors involved in apoptosis. Two major pathways of caspase activation have been described in mammalian cells, resulting in apoptosis. In the mitochondrial pathway Bax and Bid are cell death factors, which increase mitochondrial permeability and release of cytochrome C. Cell survival factors Bcl-2, Bcl-XL, and BAG-1 inhibit actions of Bax and Bid on mitochondria. Apaf-1, a downstream mediator of apoptosis, along with cytochrome C, associates with caspase 9 in cytoplasm and leads to its activation. The resultant apoptosome initiates a cascade of effector caspases, which include caspases 3, 6, and 7. Active caspase 3 activates DNA fragmentation factor and promotes internucleosomal cleavage of DNA. The death receptor pathway is triggered by members of the death receptor superfamily such as CD95 and tumour necrosis factor receptor. Formation of a death inducing signalling complex induces caspase 8 activation and thereby the downstream caspase cascade. Further control of the apoptotic process is provided by inhibitors of apoptosis in the cytoplasm that abrogate caspase activity.Interaction between the two pathways exist. P53 is known to induce apoptosis, but exact mechanisms are not clear. The mitochondrial pathway seems to dominate in breast cancer