Figure 1. Clinical phenotypes of Proband 1 and 2.
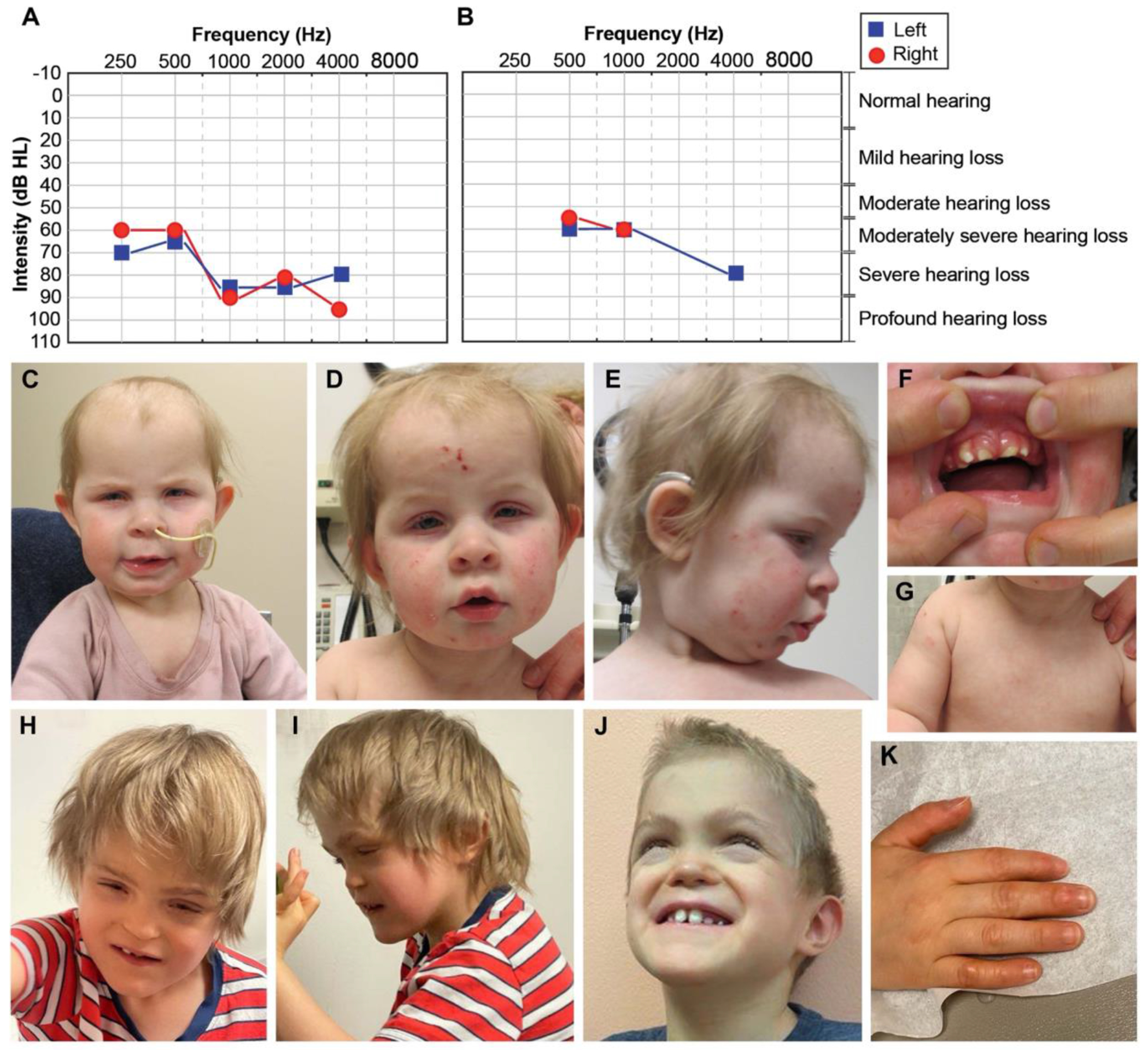
(A) Proband 1’s visual reinforcement audiometry (VRA) test completed at 17 months of age using insert headphones and warble tones. Air conduction thresholds from this test revealed moderately severe to profound hearing loss in the right ear, and moderately severe to severe hearing loss in the left ear. (B) Air conduction thresholds from Proband 2’s auditory brainstem response (ABR) test at 7 years of age indicated moderate to moderately severe hearing loss for the right ear and moderately severe to severe hearing loss for the left ear. (C-D) Face of Proband 1 at 10 months-1.5 years. In C and D note high forehead, macrotia, deep-set eyes, blepharophimosis, blepharitis (yellow crust on lashes), and bitemporal narrowing. In D and E note inflammation and excoriation marks from atopic dermatitis involving the whole face. In E note upturned nose and depressed nasal bridge. (F) Mouth of Proband 1. Note misaligned teeth and thickened gums. (G) Chest of Proband 1. Note athelia (absent nipples). (H-J) Face of Proband 2 at 6-7.5 years. Note brachycephaly, midface hypoplasia, narrow and long palpebral fissures, lagophthalmos (incomplete closure of eyelids), depressed nasal bridge, short philtrum, simplified ears, prominent chin, abnormal dentition, and misaligned teeth. (K) Hand of Proband 2. Note callused digits.
