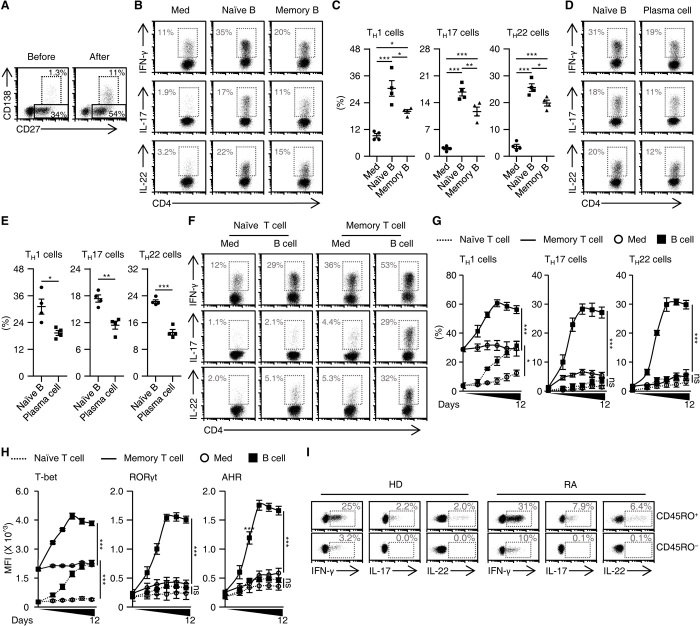
Fig. 2. Naïve B cells are more potent B cell subpopulations in triggering memory inflammatory TH subsets.
(A) Purified total B cells were cultured with T cells for 7 days in the presence of TCR triggering. The differentiation of B cells before and after coculture was analyzed by FACS (n = 3). (B to E) Purified T cells were cultured in medium or with naïve or memory B cells (B and C), or with naïve B cells or plasma cells (D and E) for 7 days as described in Materials and Methods. Expression of IFN-γ, IL-17, and IL-22 in TH cells was detected by FACS (each n = 4). (F to H) Purified naïve or memory T cells were cultured in medium or with autologous total B cells for 7 days (F) or indicated times (G and H), as described in Materials and Methods. Expression of inflammatory cytokines (F and G) and transcription factors (H) in CD4+ T cells was detected by FACS (n = 4 for each). (I) FACS analysis of IFN-γ, IL-17, and IL-22 in naïve (CD45RO−) or memory (CD45RO+) TH cells from blood of healthy donors and RA patients (each n = 3). Data are presented as means ± SEM of four independent experiments (C, E, G, and H). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001 [one-way ANOVA test for (C), (G), and (H); unpaired Student’s t test for (E)].