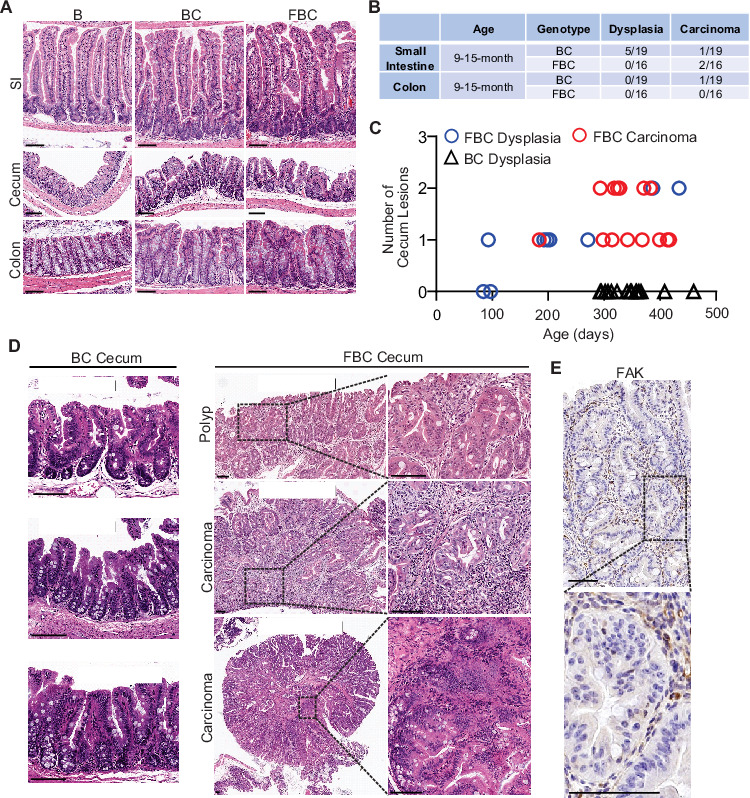
Figure 2. Fak loss enhances BRAFV600E-driven cecal tumorigenesis in mice.
(A) Representative hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of the small intestine, cecum, and colon from indicated 6-week-old mice. (B) Summary of tumor incidence at small intestine and colon in indicted mice at the indicated age. (C) Summary of tumor incidence and tumor stage at cecum in indicated mice at the indicated age. (D) H&E staining of the cecum in BC mice and cecal serrated adenoma/polyp and carcinoma in FBC mice at the indicated age. (E) Representative IHC staining of Fak in cecal tumors in FBC mice. Scale bars: 100 µm.