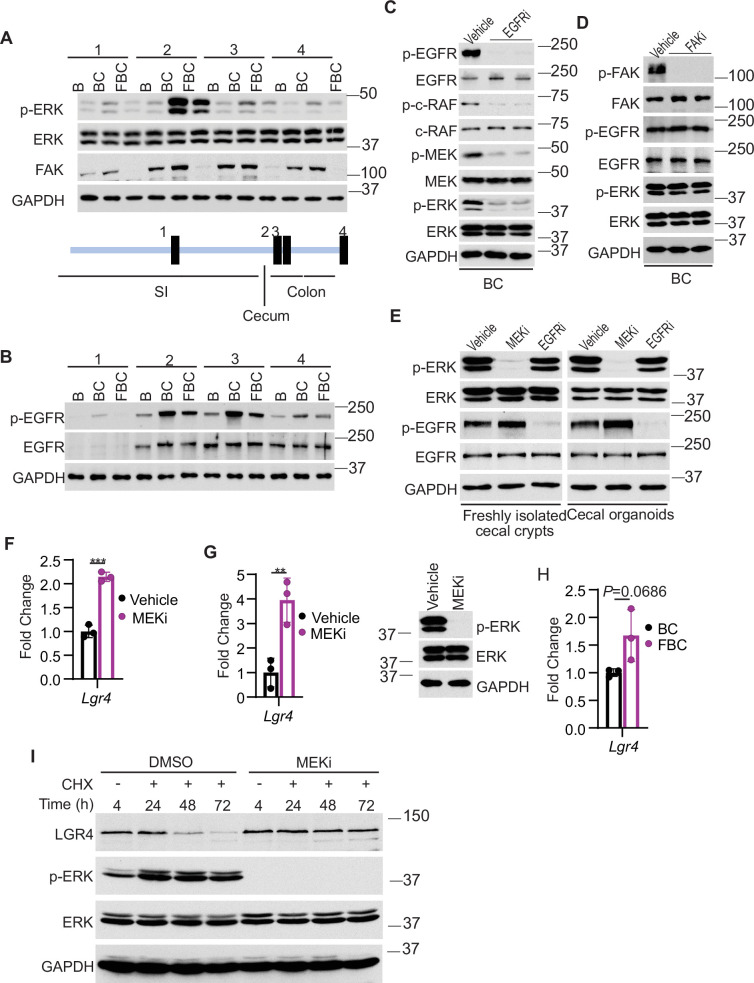
Figure 5. Fak loss inhibits ERK phosphorylation and upregulates Lgr4.
(A andB) Immunoblotting analysis of intestinal mucosa lysates from indicated bowel subsites in indicated 6-week-old mice. (C) Immunoblotting analysis of cecum lysates from 6-week-old BC mice treated with vehicle or EGFR inhibitor erlotinib for 4 hr. Each lane represented a single mouse. (D) Immunoblotting analysis of cecum lysates from 6-week-old BC mice treated with vehicle or FAK inhibitor PF-562271 for 4 hr. Each lane represented a single mouse. (E) Immunoblotting analysis of lysates from freshly isolated cecal crypts and cecal organoids treated with DMSO, MEK inhibitor PD0325901, or erlotinib, respectively as described in Methods. (F) qRT-PCR of Lgr4 using lysates from HT-29 cells treated with the vehicle and MEKi for 4 hr. Data presented as mean ± SD (***p<0.001; Student’s t-test, two-tailed). (G) qRT-PCR of Lgr4 using cecum lysates from BC mice treated with vehicle or MEKi for 6 hr. Data presented as mean ± SD (**p<0.01; Student’s t-test, two-tailed). Abrogation of ERK phosphorylation at T202/Y204 in the cecum was confirmed by western blot. (H) qRT-PCR of Lgr4 in cecum from BC and FBC mice (n=3 per group). Data presented as mean ± SD (p value calculated using two-tailed Student’s t-test). (I) Immunoblotting analysis of the lysates from HT-29 cells treated with cycloheximide (100 μg/ml) and/or MEK inhibitor PD0325901 (10 μM) as indicated.
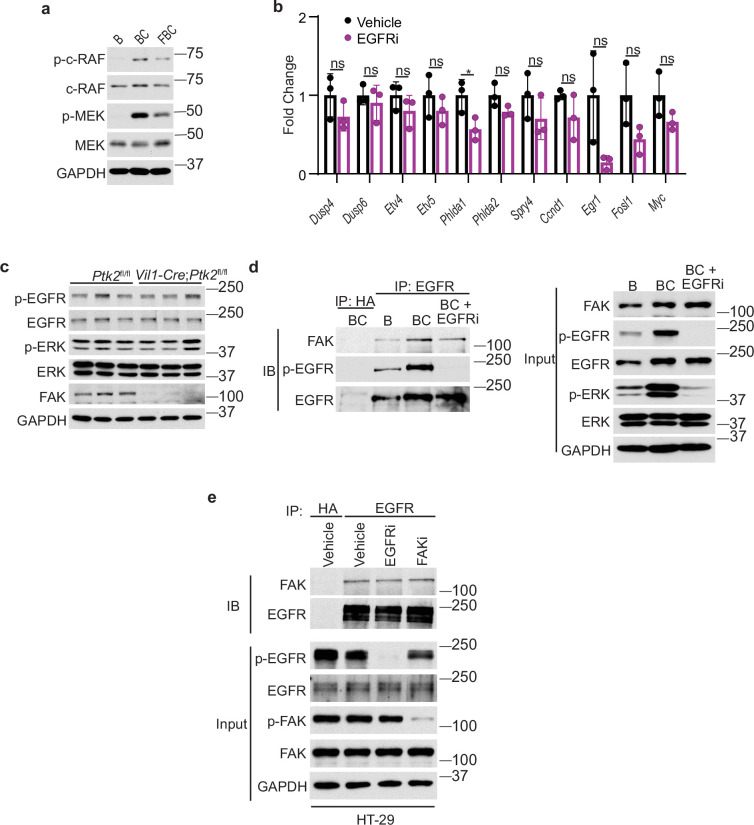
Figure 5—figure supplement 1. Fak loss downregulates BRAFV600E-induced ERK phosphorylation.
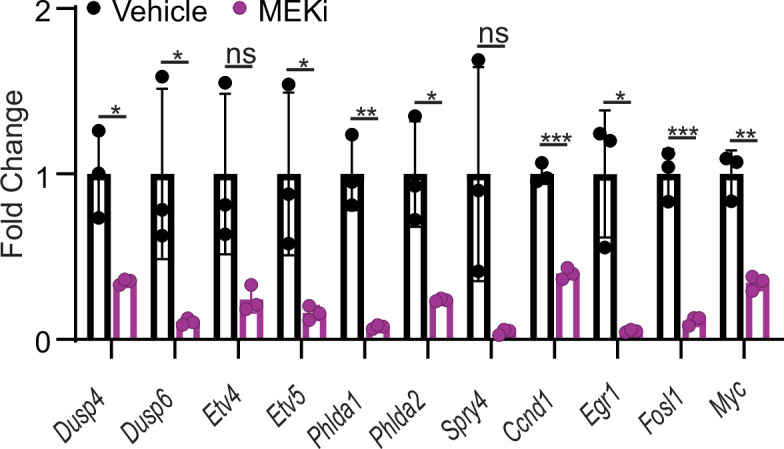
Figure 5—figure supplement 2. qRT-PCR of selected ERK transcriptional output markers in cecum from vehicle- and MEKi-treated BC mice (n=3 per group).