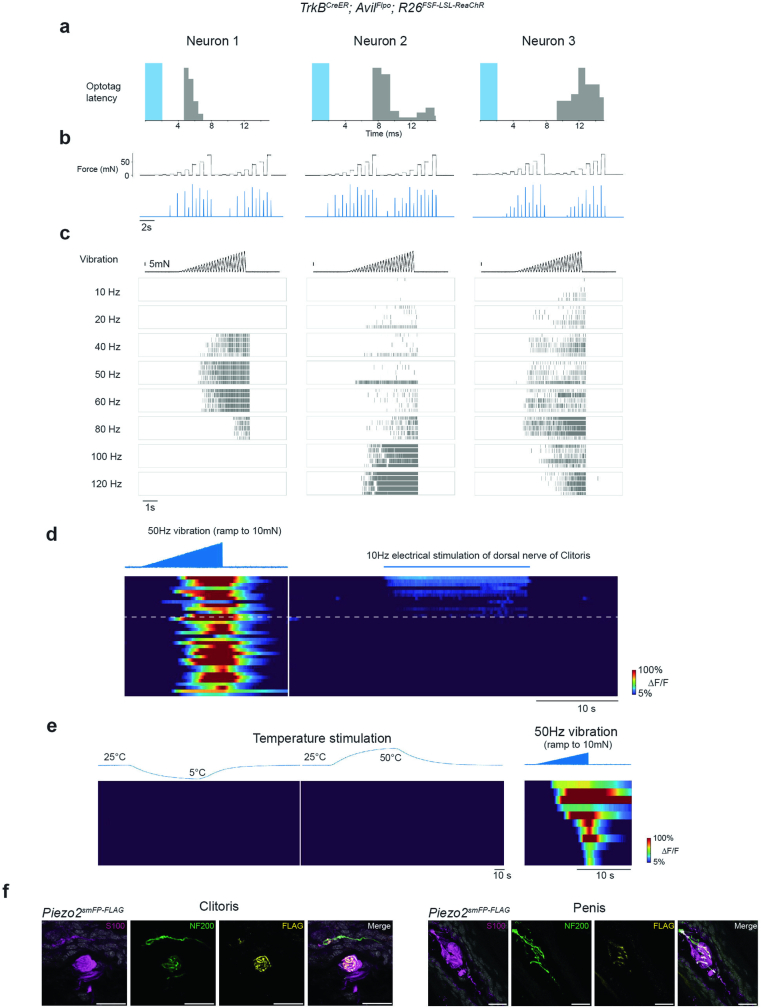
Extended Data Fig. 6. Krause corpuscle afferents are mechanosensitive neurons tuned to dynamic, light touch and mechanical vibration.
a-c, Additional examples of optotagged TrkB+ Krause corpuscle afferents. a, Latency of spikes recorded in the DRG after optogenetic activation (2 ms pulse, shown in blue) of neurons labelled in TrkBCreER; AvilFlpo; R26FSF-LSL-ReaChR male mice. b, Firing rates in response to step indentation of the glans penis. c, Raster plots of the response to ramping vibratory stimuli (example shown on top) of different frequencies from five repeated trials. d, Calcium signals of TrkB+ neurons in L6 DRG in response to ramping vibration stimuli applied to the protrusion where the clitoris is located (left) and to electrical stimulation of the dorsal nerve of the clitoris (right). Neurons responding to the electrical stimulation were identified as clitoris-innervating neurons (above the dashed line). The neurons below the dashed line are presumed to innervate the adjacent hairy skin. The neurons shown in d are from three female mice. e, Left: thermal responses of TrkB+ afferents that innervate the penis. The top trace shows the measured temperature of the water bath in which the penis was submerged. Right: the response of the same group of neurons to vibration applied to the glans penis. f, Representative images of Piezo2 expression in the axons innervating Krause corpuscles from Piezo2smFP-FLAG animals. Similar results were observed in more than 3 animals for each condition. Sections were immunostained for S100, NF200, and FLAG. Scale bar: 20 µm.