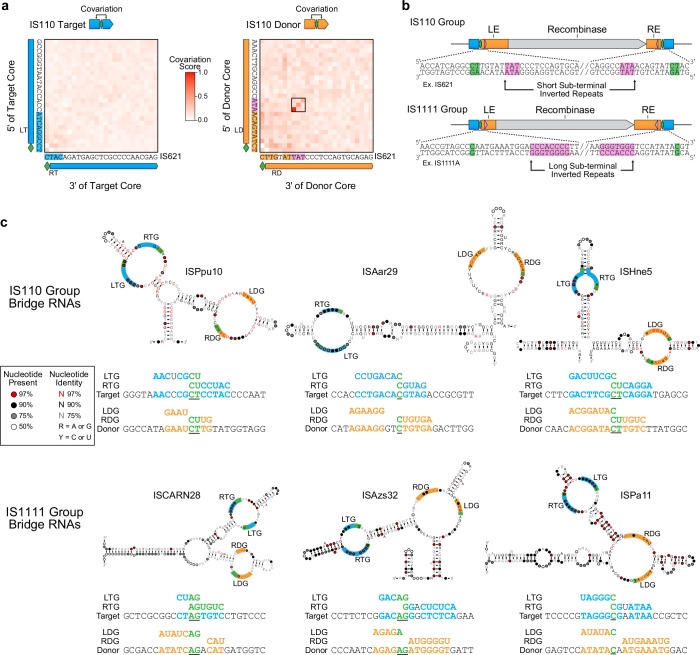
Extended Data Fig. 10. Detailed analysis of diverse bridge RNA sequences and their predicted target and donor binding patterns.
a, Covariation analysis of IS110 donor sequences identifies a short STIR. Target and donor sequences were analysed using the same covariation analysis introduced in Fig. 2b. Target sequences have no notable covariation signal while donor sequences have a prominent 3-base covariation signal that corresponds with an LT-flanking ATA tri-nucleotide and a RD-flanking TAT tri-nucleotide. b, Schematic depicting sequence features of IS110 and IS1111 group elements. IS110 are characterized by long LEs, short REs, and short STIRs. IS1111 are characterized by short LEs, long REs, and long STIRs. c, Six diverse bridge RNAs and their predicted binding patterns. The bridge RNA consensus structures shown are the same as those presented in Fig. 6d, but with more detail. Secondary structures are shown with internal loops coloured according to the sequence that they complement - target (blue), donor (orange), or core (green). Three members of each IS110 group are shown. For each of the six sequence elements catalogued in ISfinder - ISPpu10, ISAar29, ISHne5, ISCARN28, ISAzs32, and ISPa11 - IS element boundaries were inspected to identify possible base-pairing between the loops, the targets, and the donors. Under each structure, the predicted LTG, RTG, target, LDG, RDG and donor are all shown and aligned with respect to the core (underlined in black).