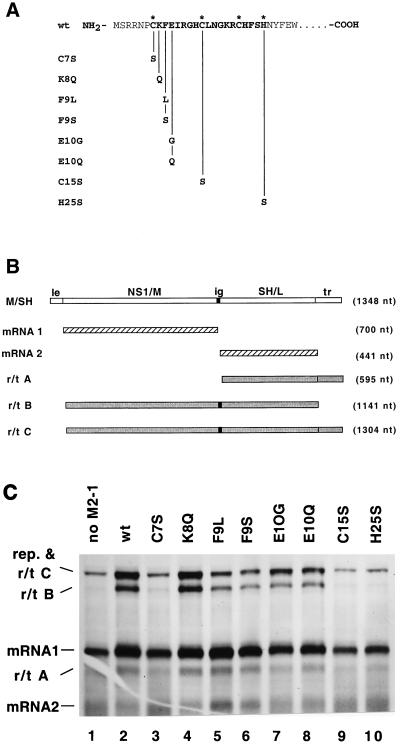
FIG. 1.
Analysis of the effects of mutations in the Cys3-His1 motif of the M2-1 protein on RS virus transcription. (A) Diagram of the mutations made in the Cys3-His1 motif. NH2 signifies the amino terminus of the M2 protein. The predicted zinc-coordinating residues are identified by an asterisk. (B) Diagram of the RS virus dicistronic subgenomic replicon containing the M/SH intergenic junction used in the transcription assay and the potential products of transcription. le, leader; ig, intergenic junction; tr, trailer; nt, nucleotide. (C) Products of RNA synthesis from the M/SH subgenomic replicon in the presence of wild-type (wt) or mutated M2-1 proteins. Cells infected with recombinant MVA vaccinia virus expressing T7 RNA polymerase were transfected with pM/SH, pN, pP, pL, and plasmids bearing genes expressing wild-type protein or mutant M2-1 proteins as indicated. Cells were exposed to [3H]uridine in the presence of actinomycin D and cytosine arabinoside. Total RNA was phenol extracted, ethanol precipitated, and analyzed by agarose-urea gel electrophoresis followed by fluorography. rep, replication products.