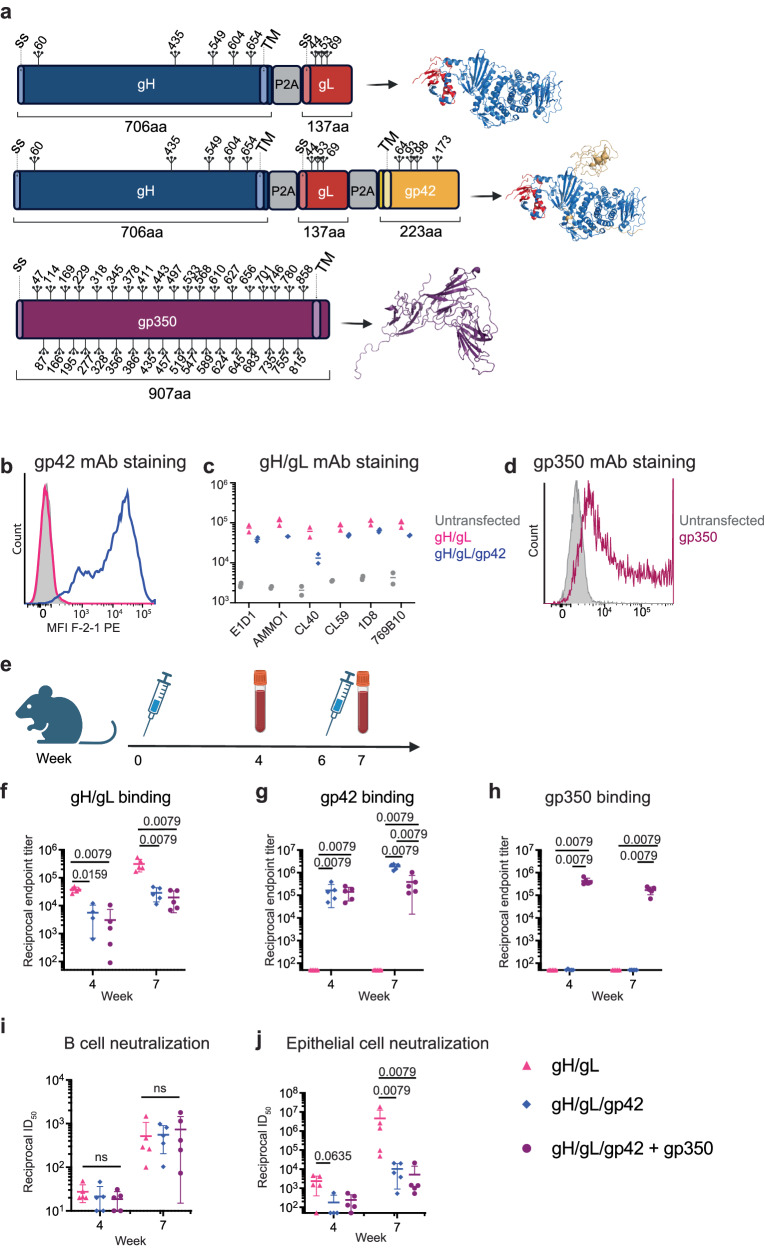
Fig. 1. Development and immunogenicity of repRNAs encoding EBV gH/gL, gH/gL/gp42, and gp350.
a 2D-schematics representing repRNA inserts encoding gH and gL, gH, gL, and gp42, or gp350. For tandem constructs, each glycoprotein is separated by a P2A peptide as indicated. Signal sequences (SS), transmembrane domains (TM), and positions of putative N-linked glycosylation sites are indicated. The expected 3D polypeptides are depicted to the right of each 2D schematic. The 3D gH/gL and gH/gL/gp42 complexes were created using PyMOL based on PDBID 6C5V. The 3D structure of gp350 was created using PyMOL based on PDBID 2H6O. b Staining of 293 cells transfected with repRNAs encoding gH/gL and gH/gL/gp42 with the anti-gp42 mAb F-2-1. c 293 cells from (b) were stained with a panel of anti-gH/gL mAbs as indicated. Each dot represents the mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of a technical replicate (n = 3). The MFI of PE-positive cells is shown for gH/gL and gH/gL/gp42 while the PE-MFI of all cells is shown for the transfected control. d Staining of 293 cells transfected with repRNA encoding gp350 with the anti-gp350 mAb 72A1. e Immunization and bleed schedule for evaluating the repRNA constructs in (a). Reciprocal endpoint binding titers to gH/gL (f), gp42 (g), or gp350 (h) in sera at weeks 4 and 7 measured by ELISA as indicated. The ability of sera from mice immunized with repRNA encoding gH/gL, gH/gL/gp42, or gH/gL/gp42 + gp350 to neutralize EBV infection of B cells (i), or epithelial cells (j) as indicated. Each dot represents an individual mouse (n = 5), the horizontal bars represent the means, and the error bars represent the standard deviation in (f–j). Statistical differences were determined using a Mann-Whitney Test. a and e were created using BioRender.com.