Fig. 2. The configuration of the two-stack G-quadruplex provides an unusual topology with triplet formation stabilizing the bases directly above the top G tetrad.
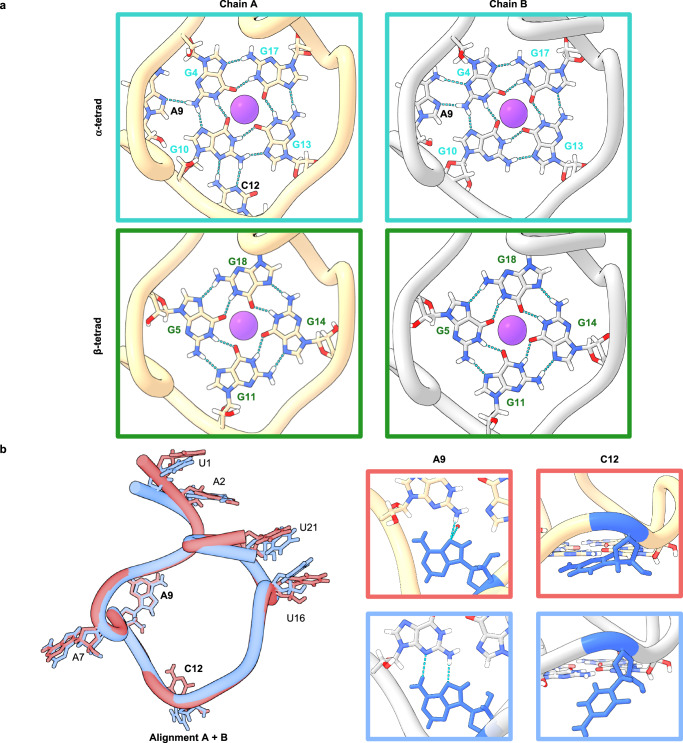
a Guanosine interactions in the α- and β-tetrads and the loop-base to tetrad stabilization of the α-tetrad. Chain A (left) shows the α-tetrad is stabilized through noncanonical hydrogen bonding in the A9 loop between A9 and G4 and the C-loop between C12 and G10. In Chain B (right) the α-tetrad is stabilized through noncanonical hydrogen bonding in the A9 loop between A9 and G4. b Alignment of Chain A in red and Chain B in blue (left) illustrates overall structural similarities between the two copies. Residues with a high degree of overlap have been omitted. A9 and C12 have minor changes in bonding interactions (right). In Chain A, C12 (blue) is observed in the downward position contacting the G10 of the α-tetrad while in Chain B, C12 (blue) is observed in the upward position extending into the solvent environment.