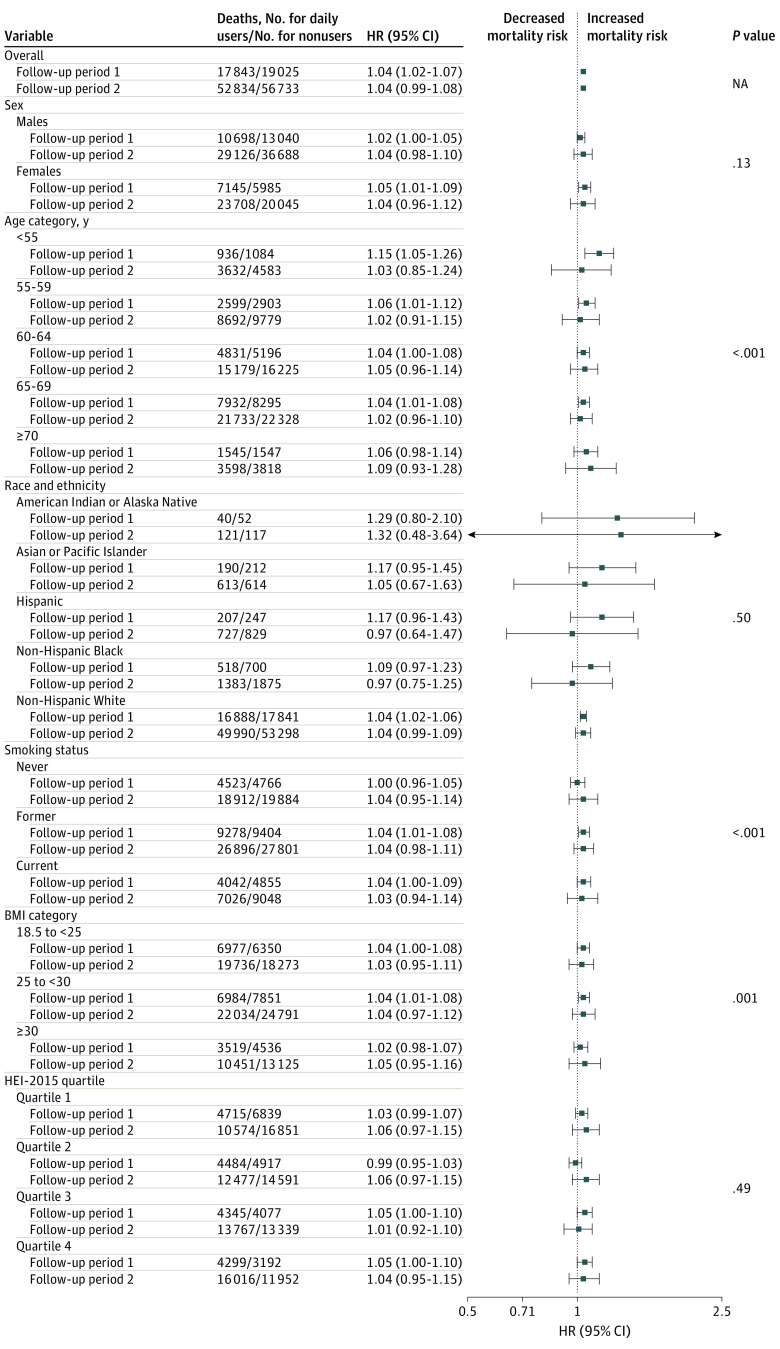
Figure 1. Stratified Baseline Estimates for the Association of Daily Multivitamin Use and All-Cause Mortality (N = 390 124).
The proportional hazards assumption was violated (P < .001). Therefore, follow-up time was stratified by the midpoint, and hazard ratios (HRs) were calculated using an interaction term between follow-up period and the exposure variable. Follow-up period 1 was the first 12 years of follow-up, and follow-up period 2 was the last 15 years of follow-up. P value represents the significance of the likelihood ratio test of each effect modifier. Models were stratified by study and adjusted for sex (male or female), age at enrollment (years), race and ethnicity, education (≤11 years; 12 years, completed high school or General Educational Development; post–high school training; some college; college and postgraduate; or other), body mass index (BMI; calculated as weight in kilograms divided by height in meters squared) category, marital status (married or living as married, divorced or separated, widowed, or never married), smoking status (never smoker, former smoker, current smoker ≤20 cigarettes/d, current smoker 21-40 cigarettes/d, or current smoker >40 cigarettes/d), alcohol consumption (0 drinks per day, <1 drink/d, 1 to <2 drinks/d, 2 to <3 drinks/d, ≥3 drinks/d), physical activity level (never, low, moderate, high), coffee intake (0 cups/d, <1 cup/d, 1 cup/d, 2-3 cups/d, 4-5 cups/d, or ≥6 cups/d), family history of cancer (yes or no), Healthy Eating Index 2015 (HEI-2015) quartile (quartile 1, 21.55 to <60.90; quartile 2, 60.90 to <68.00; quartile 3, 68:00 to <74.20; quartile 4, 74.20 to <96.10), and use of individual supplements (yes or no). NA indicates not applicable.