Table 1.
The variety of reactions catalysed by ADHs.
| No. | Reaction | Scheme | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 |
Alcohol oxidation |
 |
[23] |
| 2 |
Carbonyl reduction |
 |
[[24], [25], [26]] |
| 3 |
Aldehyde oxidation |
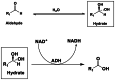 |
[27] |
| 4 | Aldehyde dismutation | 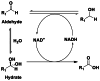 |
[[28], [29], [30], [31]] |
Note: direct aldehyde oxidation to the carboxylic acid is normally only observed under NADH recycling conditions when NADH concentrations are low. Prior hydration of the aldehyde is shown (reaction 3) for aldehyde oxidation. The hydration produces a gem-diol which is structurally analogues to a secondary alcohol. The oxidation of the hydrated aldehyde to form a carboxylic acid is not reversible.
