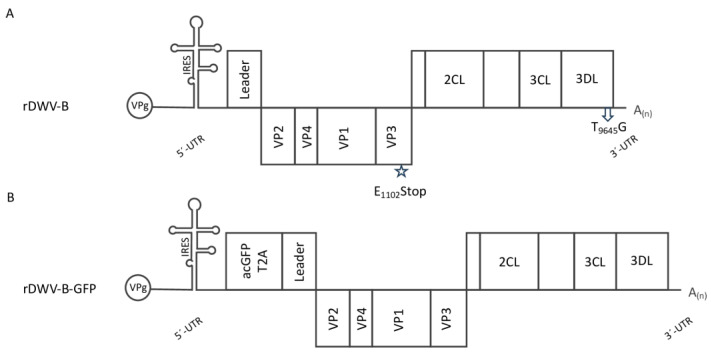
Figure 1.
Molecular DWV-B clones used in this study. (A) The genome organization of rDWV-B is illustrated. Captions encompass the genome-linked protein (VPg), the 5′-UTR featuring an IRES element, the leader protein gene (Leader), the structural protein gene cassette (VP1-VP4), and the nonstructural protein gene cassette containing annotated functional enzymes (2CL, 3CL, and 3DL), along with so-far-uncharacterized gene products (represented by empty boxes), and the short 3′-UTR with the poly-A-tail (A(n)). A star highlights the mutation of one amino acid codon (G4459AG to T4459AG), resulting in the alteration of E1102 to a termination signal (E1102Stop). This mutation leads to an interruption of the reading frame, rendering the genome non-replicative. An arrow indicates the synonymous mutation T9645G, which disrupts an XhoI restriction enzyme cleavage site without altering the encoded amino acid (G9643CT to G9643CG). (B) The genome organization of rDWV-B-GFP follows a similar structure with corresponding captions. However, it incorporates an additional acGFP gene and a T2A peptide preceding the viral ORF.