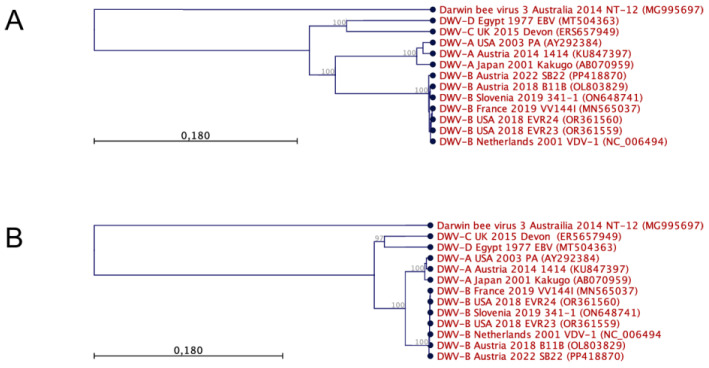
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic analyses of DWV genomes and gene products were conducted using nucleotide (A) and polyprotein sequence (B) alignments employing UPGMA tree construction methods. Each virus is identified by its respective master variant, country of origin, year of isolation, strain designation, and accession number. The viruses were predominantly isolated from Apis mellifera, except for VDV-1, originating from Varroa destructor mites, and VV144I, obtained from Vespa velutina. The relationships between the species are illustrated in an unrooted increasing phylogram, with node numbers indicating bootstrap values derived from 1000 replicates in percentages. Scale bars represent the number of substitutions per site. Notably, the analysis reveals the distinct separation of individual master variants, close relationships among master variants, and a shared ancestry of DWVs.